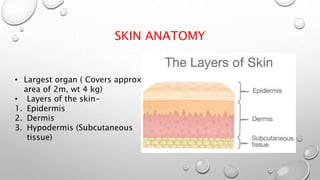
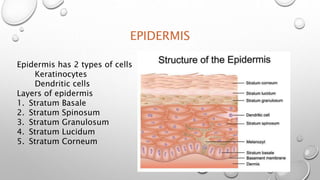
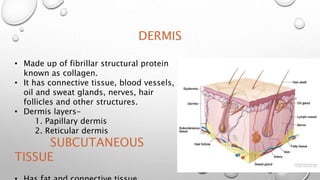
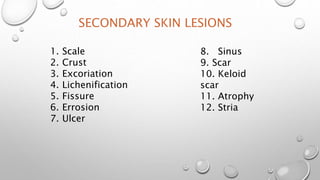
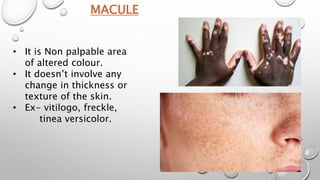
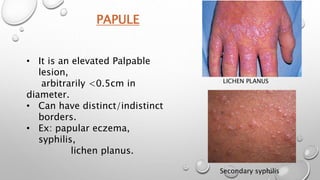
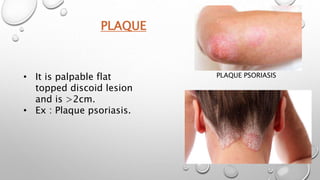
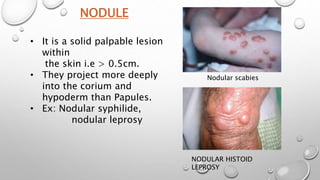
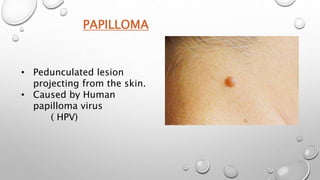
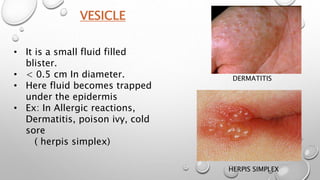
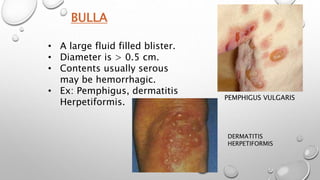
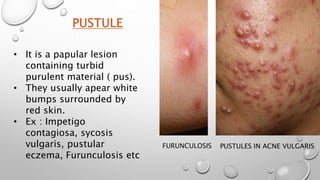
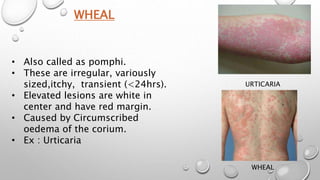
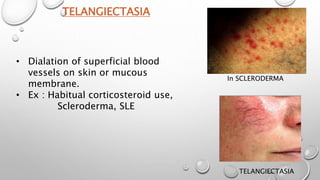
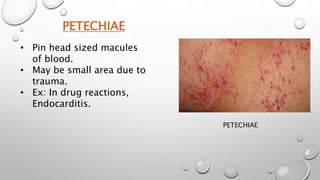
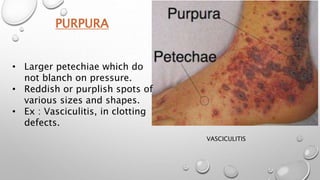
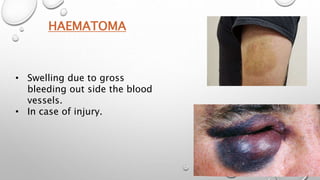
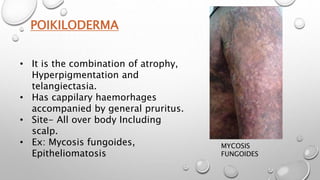
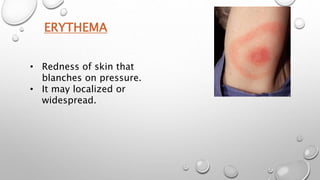
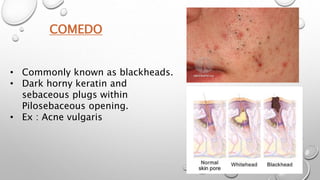
This document summarizes the anatomy and functions of the skin and describes various primary and secondary skin lesions. It discusses the layers of the skin - epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis - and their components. It then defines and provides examples of different types of primary skin lesions including macules, papules, plaques, nodules, vesicles, bullae, pustules, and wheals. Secondary skin lesions like scales, crusts, and ulcers are also outlined. The functions of the skin in protection, sensation, temperature regulation, and vitamin D production are highlighted.