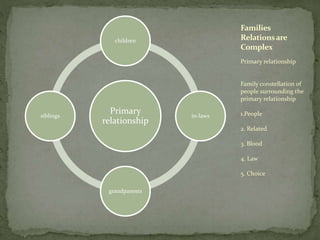
This document discusses different types of primary relationships and families. It notes that while traditionally most Americans married, rates of divorce are now around 50% and many choose not to marry. Contemporary relationships are more diverse and structured differently based on individuals' needs. Primary relationships can include marriage, domestic partnerships, or unmarried couples maintaining a relationship. Families extend beyond the primary relationship and can include children, in-laws, grandparents and other relatives through blood, law or choice. The structures of relationships and families are complex and evolving.