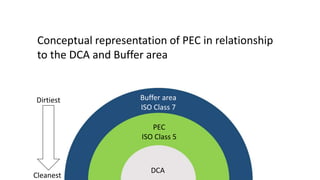
The Primary Engineering Control (PEC) provides an ISO Class 5 environment for compounding sterile preparations. A PEC is commonly a hooded work area within an ISO Class 7 buffer room that uses HEPA filtration to maintain ISO Class 5 air quality. There are three main types of PECs: laminar airflow workbenches with horizontal airflow; biological safety cabinets with vertical airflow; and compounding aseptic isolators or containment isolators, commonly called "glove boxes," which have enclosed compounding chambers that can be accessed through gloves. The key difference between compounding aseptic isolators and containment isolators is that containment isolators use negative pressure and can be used for hazardous compounding, while isolators use positive pressure and