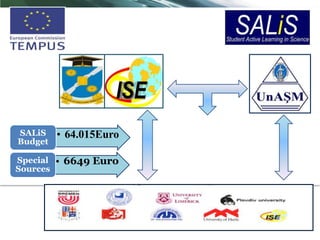
The SALIS project at the Institute of Educational Sciences aims to enhance the scientific competence of science teachers in Moldova through continuous education courses, contributing to effective science implementation in schools. It developed curricula and methodologies for teacher training in biology, chemistry, and physics, and established equipped laboratories for hands-on learning. The project also included extensive training for 323 science teachers and various resources for ongoing support and development in educational practices.