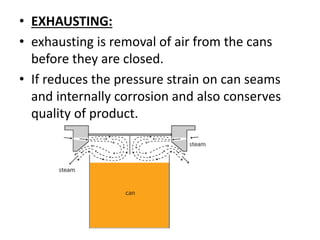
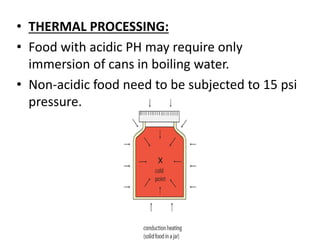
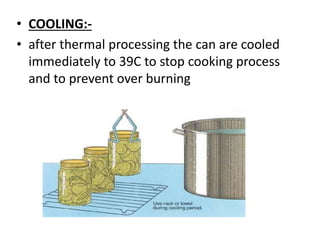
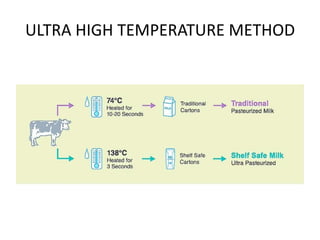
This document discusses different methods of food preservation using heat treatment, including canning, pasteurization, and sterilization. Canning involves sealing food in containers and applying heat to kill microorganisms and prevent spoilage. The process includes preparing, filling, and exhausting cans before sealing and applying thermal processing. Pasteurization uses a mild heat treatment for a brief time to eliminate pathogens and partially reduce microorganisms. Sterilization completely destroys all microorganisms using heat treatment of 121C.