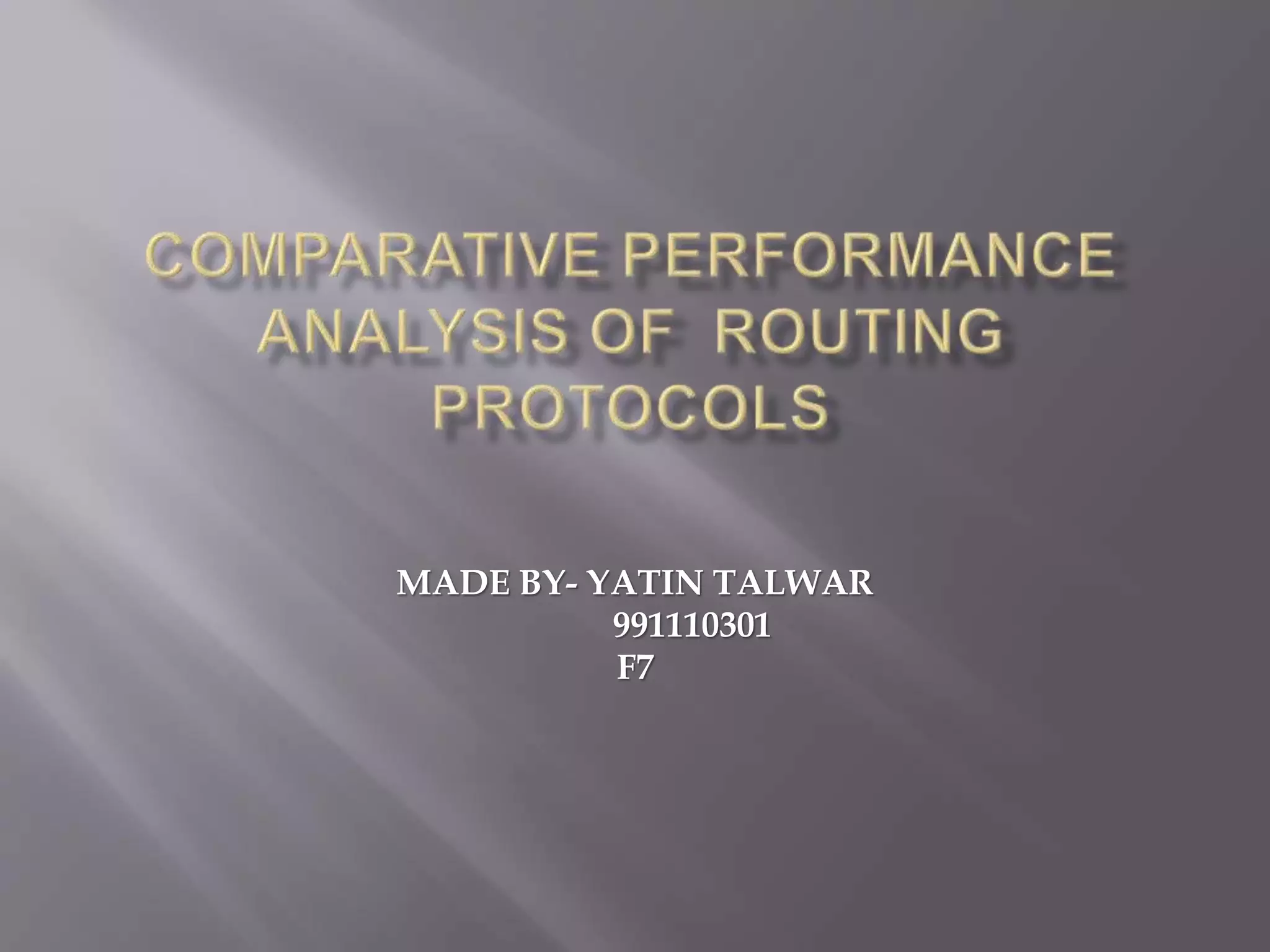
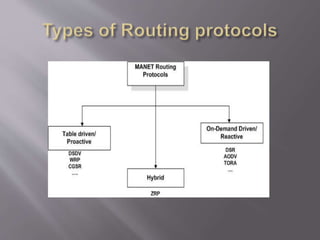
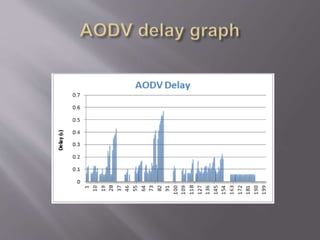
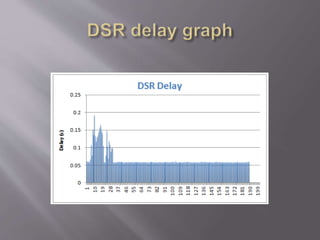
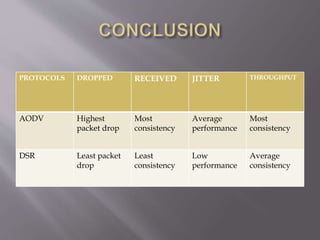
This document summarizes and compares two reactive routing protocols for wireless ad-hoc networks: AODV and DSR. It describes that AODV uses routing tables and sequence numbers to prevent loops, and broadcasts route requests containing source and destination IP addresses. DSR uses source routing by storing routes in a cache, and data packets carry the source route. The document outlines the key mechanisms of each protocol, including route discovery and maintenance for DSR. It concludes by comparing their performance based on metrics like packet drop, consistency, throughput, noting that AODV had higher drops but more consistency while DSR had lower drops but less consistency.