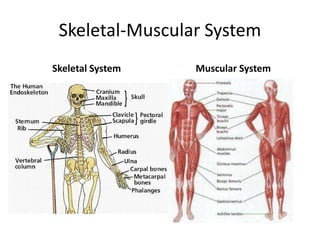
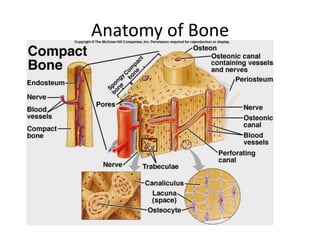
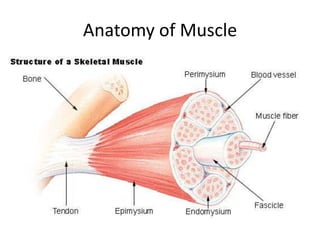
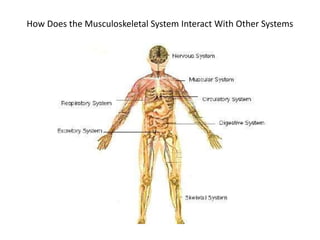
The muscular-skeletal system works together to allow movement of the body and control automatic functions. Bones provide structure, protect organs, store minerals, and produce blood cells. Muscles control movement and processes like blood flow. The systems interact with other body systems like moving to get nutrients from digestion and oxygen from respiration.