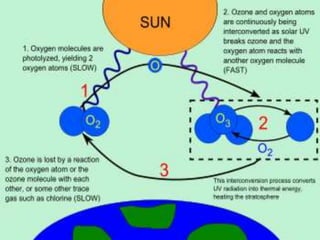
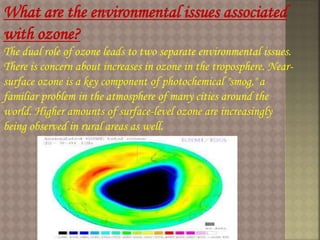
Stratospheric ozone plays a key role in absorbing ultraviolet radiation and maintaining atmospheric temperature structure. Ground-based and satellite instruments have detected significant decreases in stratospheric ozone levels over Antarctica and the Arctic regions. Increased ultraviolet radiation reaching the Earth's surface due to ozone depletion could harm human health through higher skin cancer rates and eye disease. It may also damage agriculture, forests and marine ecosystems. The primary causes of ozone depletion are emissions of ozone-depleting substances like CFCs, halons, and methyl chloroform. The Montreal Protocol agreement aims to phase out the production of these chemicals.