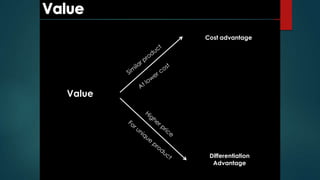
Value chain analysis examines the separate business activities that create value for customers. Activities include inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and services. Each activity adds value and the goal is to offer more value than the costs of the activities. A competitive advantage can be gained by analyzing and improving the value chain.
Tata Motors uses value chain analysis to gain efficiencies. For inbound logistics, it has long-term contracts with suppliers and uses IT for transparency. Its operations include training programs and distributed manufacturing. Outbound logistics utilizes stockyards and contracts. Marketing identifies customer needs and sales targets institutional clients. Services provides easy access to spare parts and workshops.