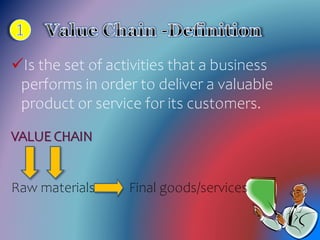
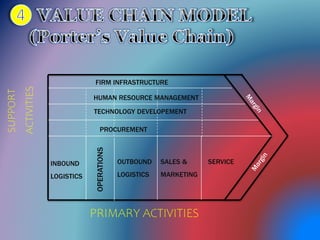
Value chain analysis examines all business activities, from procurement of raw materials to delivery of the final product or service. It aims to maximize value for customers while minimizing total costs. The value chain framework divides activities into primary and support activities. Primary activities include inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service. Support activities are firm infrastructure, human resource management, technology development, and procurement. Understanding the value chain can help businesses identify areas for improvement and create competitive advantages.