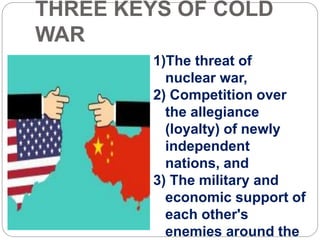
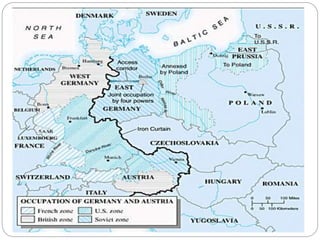
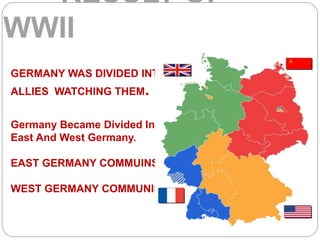
The Cold War was characterized by tensions and confrontations between the United States and the Soviet Union, which avoided escalating into a full-scale war despite numerous regional conflicts. Key features included the threat of nuclear war, competition for the allegiance of newly independent nations, and military support of opposing allies, with significant military alliances formed such as NATO and the Warsaw Pact. India maintained a policy of non-alignment, actively intervening in world politics and balancing the influence of superpowers without joining their alliances.