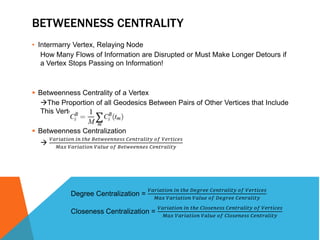
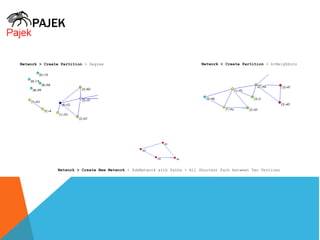
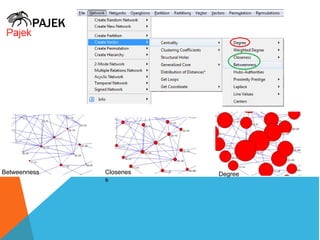
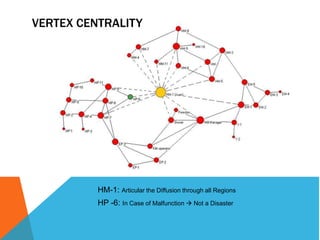
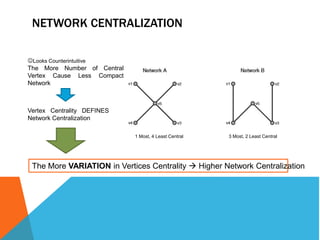
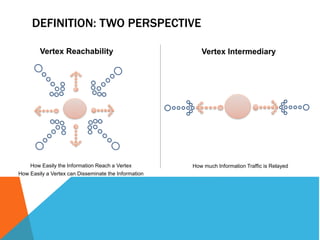
This document discusses different measures of centrality in networks: degree centrality, closeness centrality, and betweenness centrality. Degree centrality is a measure of how connected a node is based on its number of connections. Closeness centrality quantifies how close a node is to all other nodes based on the shortest path distances. Betweenness centrality measures the number of shortest paths that pass through a node, indicating its importance as an intermediary. The document also describes how to calculate centralization measures for networks based on these centrality metrics.


![DEGREE CENTRALITY: UNDIRECTED NET
• Degree Centrality of a Vertex
Vertex Degree
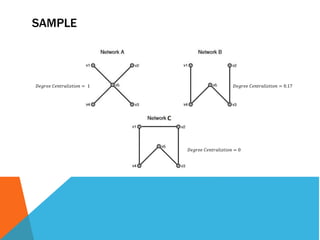
• Degree Centralization of a Network
푉푎푟푖푎푡푖표푛 푉푎푙푢푒 = 푣 [푀푎푥 퐷푒푔푟푒푒 − deg(푣)]
푀푎푥 푉푎푟푖푎푡푖표푛 푉푎푙푢푒 = 퐻푎푝푝푒푛푠 푖푛 푆푡푎푟 − 푁푒푡푤표푟푘 푖푛 푈푛푑푖푟푒푐푡푒푑 푆푖푚푝푙푒 푁푒푡푤푟표푘
퐶푒푛푡푟푎푙푖푧푎푡푖표푛 푉푎푙푢푒 =
푉푎푟푖푎푡푖표푛 푉푎푙푢푒
푀푎푥 푉푎푟푖푎푡푖표푛 푉푎푙푢푒=(푛−1)×(푛−2)
푛: 푉푒푟푡푖푐푒푠 퐶표푢푛푡
푀푎푥 푉푎푟푖푎푡푖표푛 푉푎푙푢푒 = 3 ∗ 3 − 1 + 1 ∗ 3 − 3 = 6 푀푎푥 푉푎푟푖푎푡푖표푛 푉푎푙푢푒 = 12 푀푎푥 푉푎푟푖푎푡푖표푛 푉푎푙푢푒 = 20
For Directed Network this Definition will not Work!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationslides-ch06-exploratorysocialnetworkwithpajek-141003170433-phpapp02/85/Exploratory-Social-Network-Analysis-with-Pajek-Center-Periphery-6-320.jpg)
![CLOSENESS CENTRALITY
• Degree Centrality has Local View of Vertex Neighborhood
• Global View
• Distance to all Other Vertices: The Closer Path The Faster Diffusion
• Geodesic Shortest Path Between Two Vertices
• Distance Length of Geodesic Path
• Closeness Centrality of a Vertex
퐶푣 =
푛 −1
푢≠푣 퐷푖푠푡푎푛푐푒(푢,푣)
• Closeness Centralization of a Network
푉푎푟푖푎푡푖표푛 푉푎푙푢푒 = 푣 [푀푎푥 퐶푒푛푡푟푎푙푖푡푦 − 퐶푣 ]
푀푎푥 푉푎푟푖푎푡푖표푛 푉푎푙푢푒 = 퐻푎푝푝푒푛푠 푖푛 푆푡푎푟 − 푁푒푡푤표푟푘 푖푛 푈푛푑푖푟푒푐푡푒푑 푆푖푚푝푙푒 푁푒푡푤푟표푘
푉푎푟푖푎푡푖표푛 푉푎푙푢푒
퐶푒푛푡푟푎푙푖푧푎푡푖표푛 푉푎푙푢푒 =
푀푎푥 푉푎푟푖푎푡푖표푛 푉푎푙푢푒=2 × 푛−1 ×(푛−2)
푀푎푥 퐶푣 = 1 푖푛 푆푡푎푟 − 푁푒푡푤표푟푘
푀푎푥 푉푎푟푖푎푡푖표푛 푉푎푙푢푒 = 푛 − 1 × 1 + 2 × 푛 − 2 − 1 = 24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationslides-ch06-exploratorysocialnetworkwithpajek-141003170433-phpapp02/85/Exploratory-Social-Network-Analysis-with-Pajek-Center-Periphery-8-320.jpg)