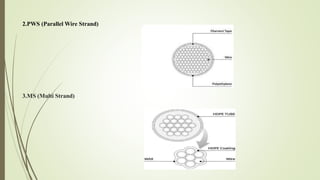
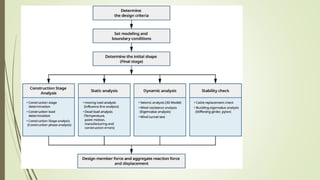
The document discusses cable-stayed bridges, providing information on their components, design considerations, advantages, and analysis methods. It introduces the Midas Civil software for bridge design and analysis. It then discusses the Durgam Cheruvu cable-stayed bridge project in Hyderabad, India, which was proposed to ease traffic congestion. Key components of cable-stayed bridges are described, including pylons, girders, cables, and anchoring systems. Methods of structural analysis for these bridges, including for construction stages, are also summarized.