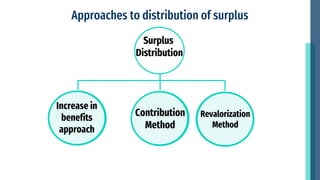
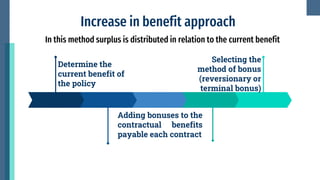
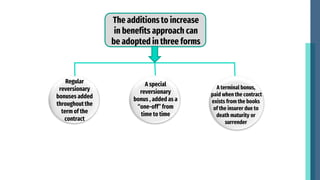
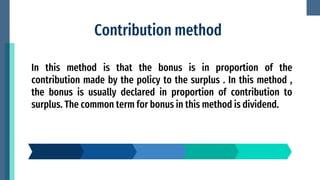
This document discusses the distribution of surplus in life insurance. It defines surplus as the amount remaining after deducting policy reserves and expenses from premiums and investment income. Surplus comes from lower than expected mortality rates, higher investment returns, and lapsed policies. Surplus can be distributed through increased benefits, contribution/dividend methods, or revalorization. Increased benefits add bonuses to existing coverage amounts. Contribution ties bonuses to each policy's surplus contribution. Revalorization expresses surplus as a percentage increase to reserves and premiums. Insurers consider policyholder expectations, equity, solvency, and legal provisions when distributing surplus.