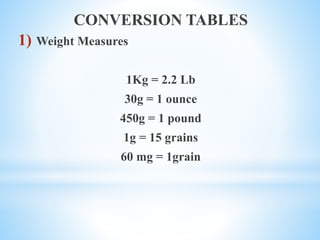
The document discusses various metrology systems including imperial and metric for measuring weight and capacity, along with conversion tables for both systems. It details percentage calculations for preparing solutions, isotonic solutions, and methods for measuring isotonicity. The document includes practical questions related to percentage solutions and the aligation method for preparing solutions of specified strengths.