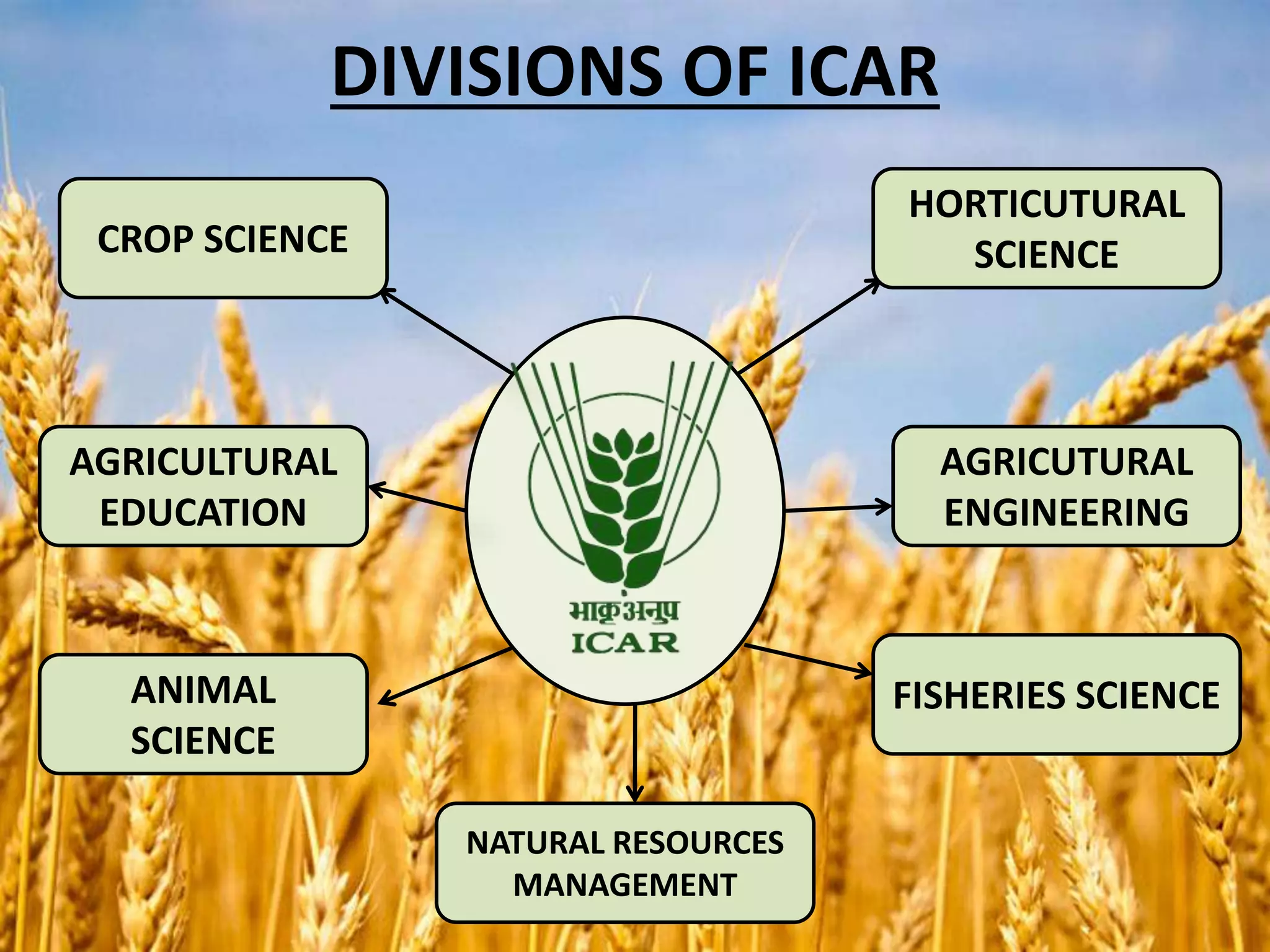
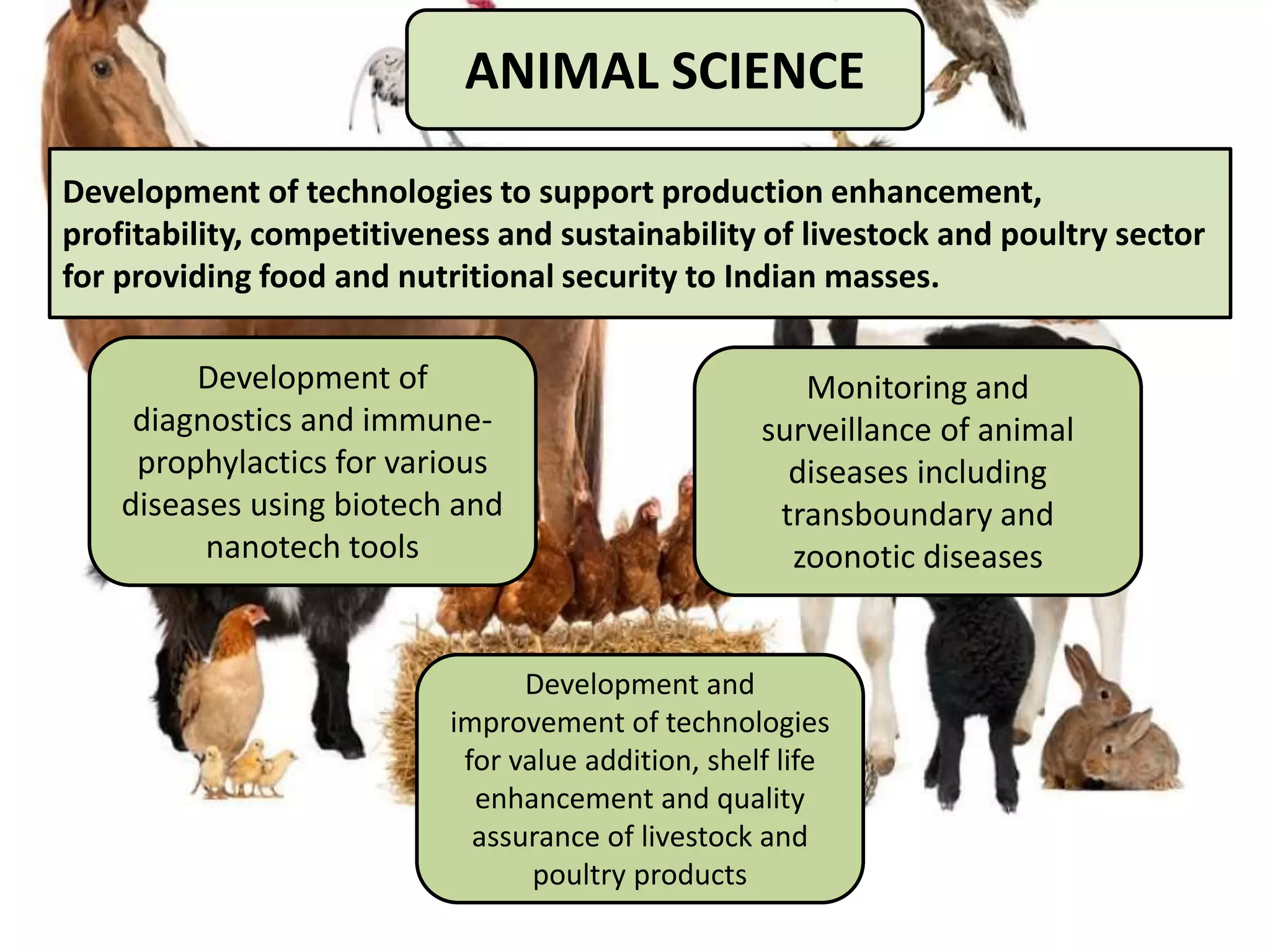
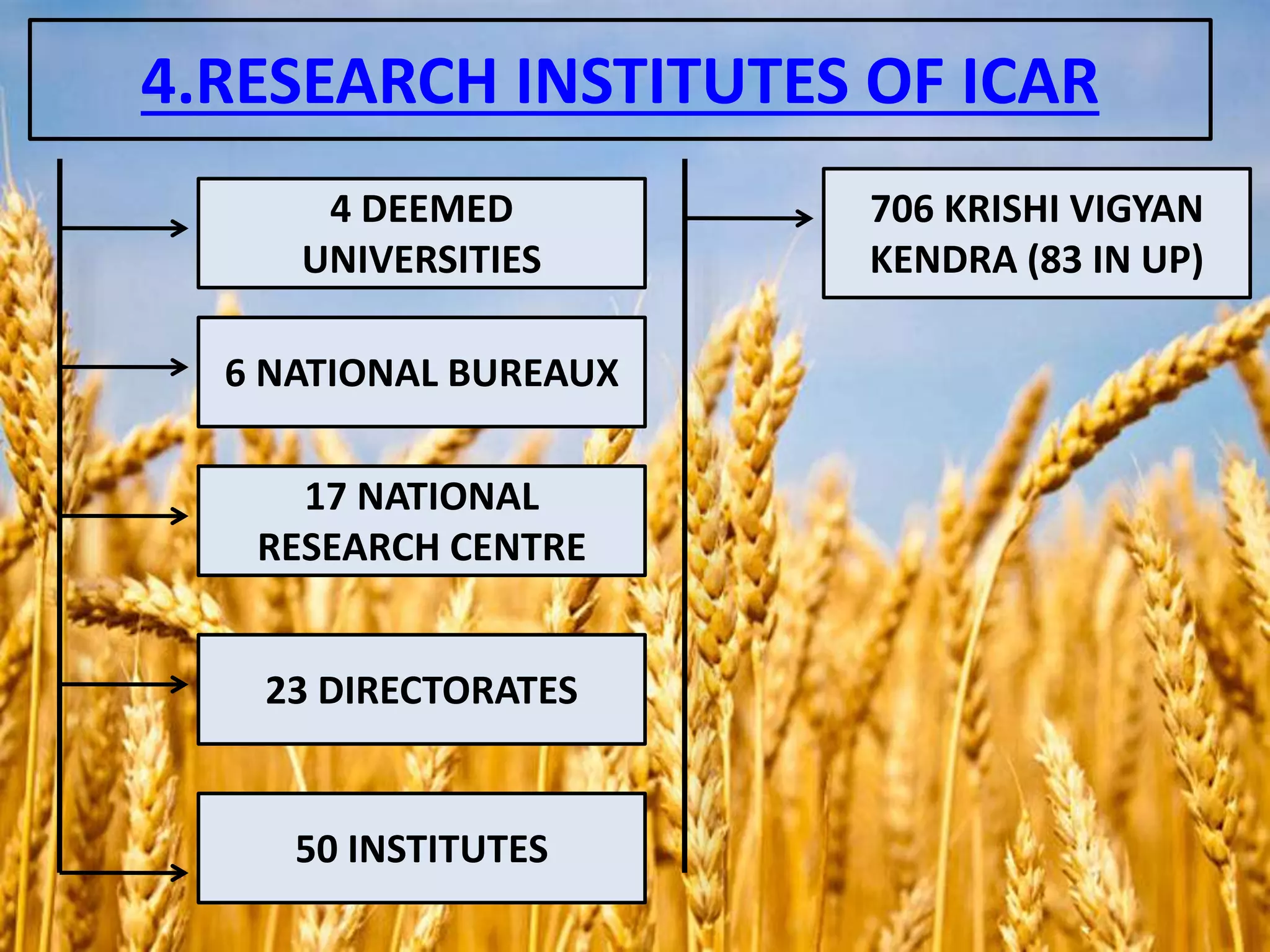
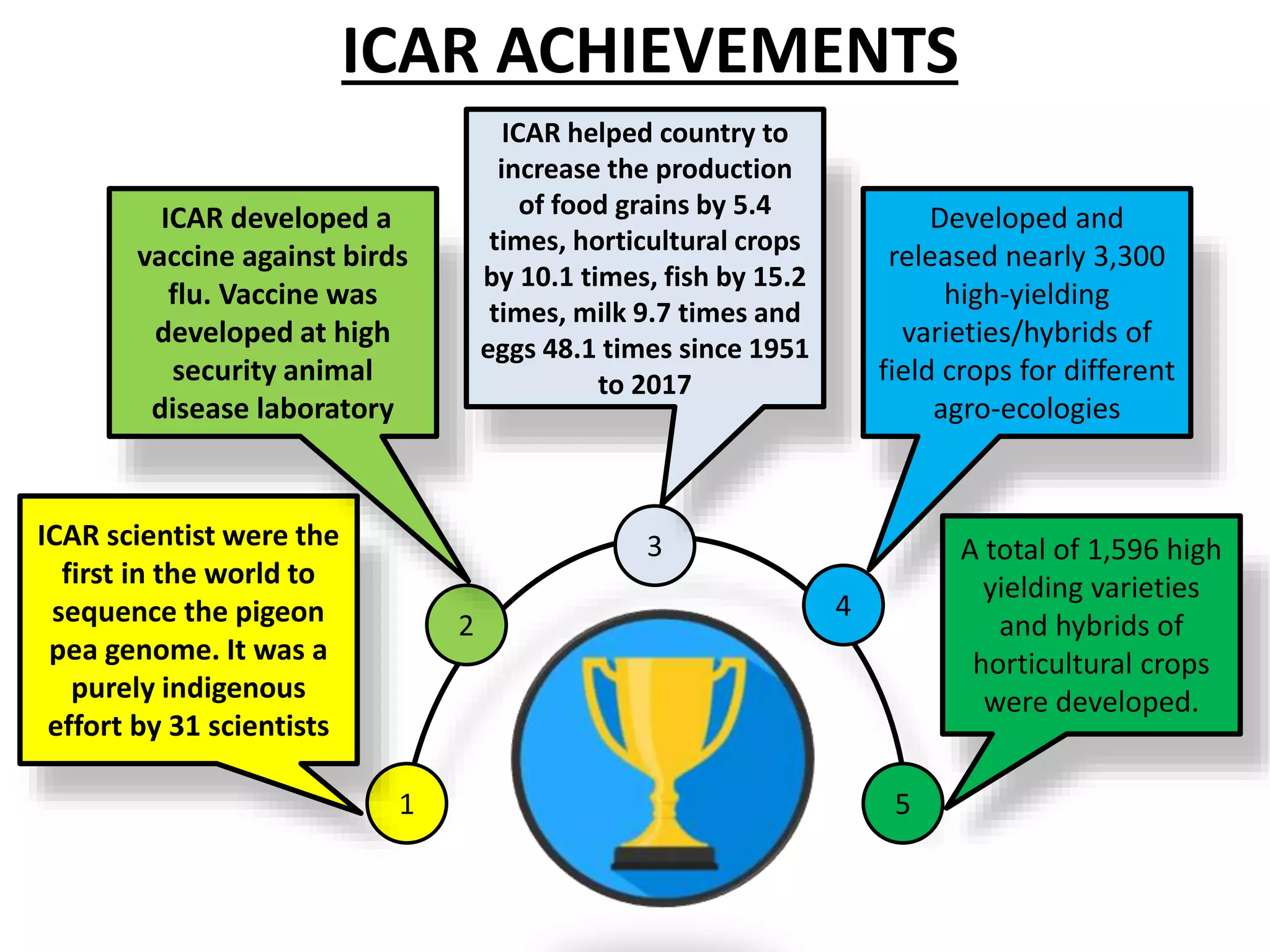
The document discusses the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR). It details that ICAR is the apex body for coordinating and managing agricultural research and education in India. It has 101 research institutes and oversees 71 agricultural universities. The document outlines ICAR's divisions which coordinate research in areas like crops, fisheries, animals, and natural resources. It also lists some of ICAR's achievements, such as increasing food grain production in India and developing thousands of high-yielding crop varieties.