This document provides an overview of elephants, including their:
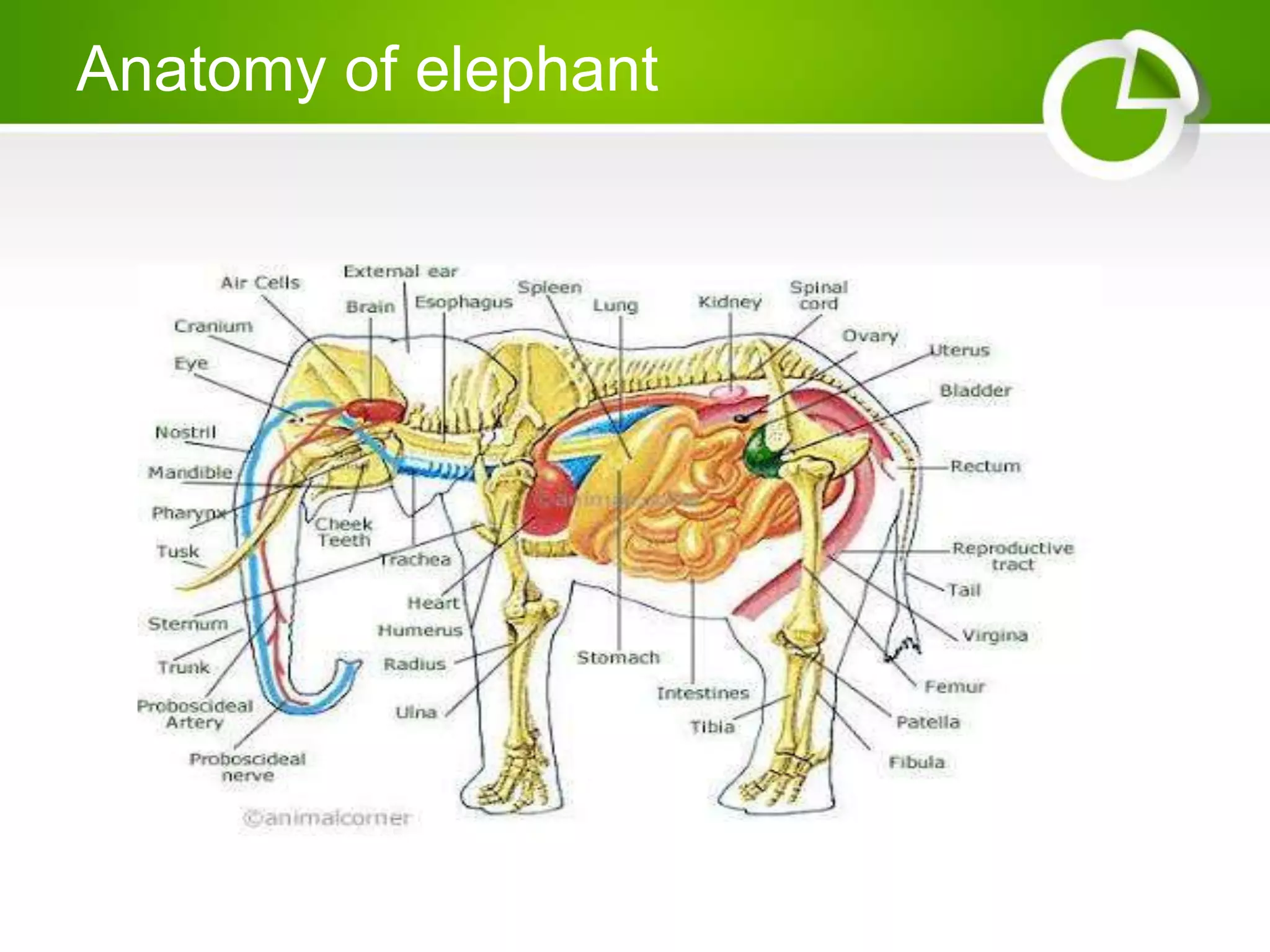
- Scientific classification and anatomy, with details on their trunk and terminology.
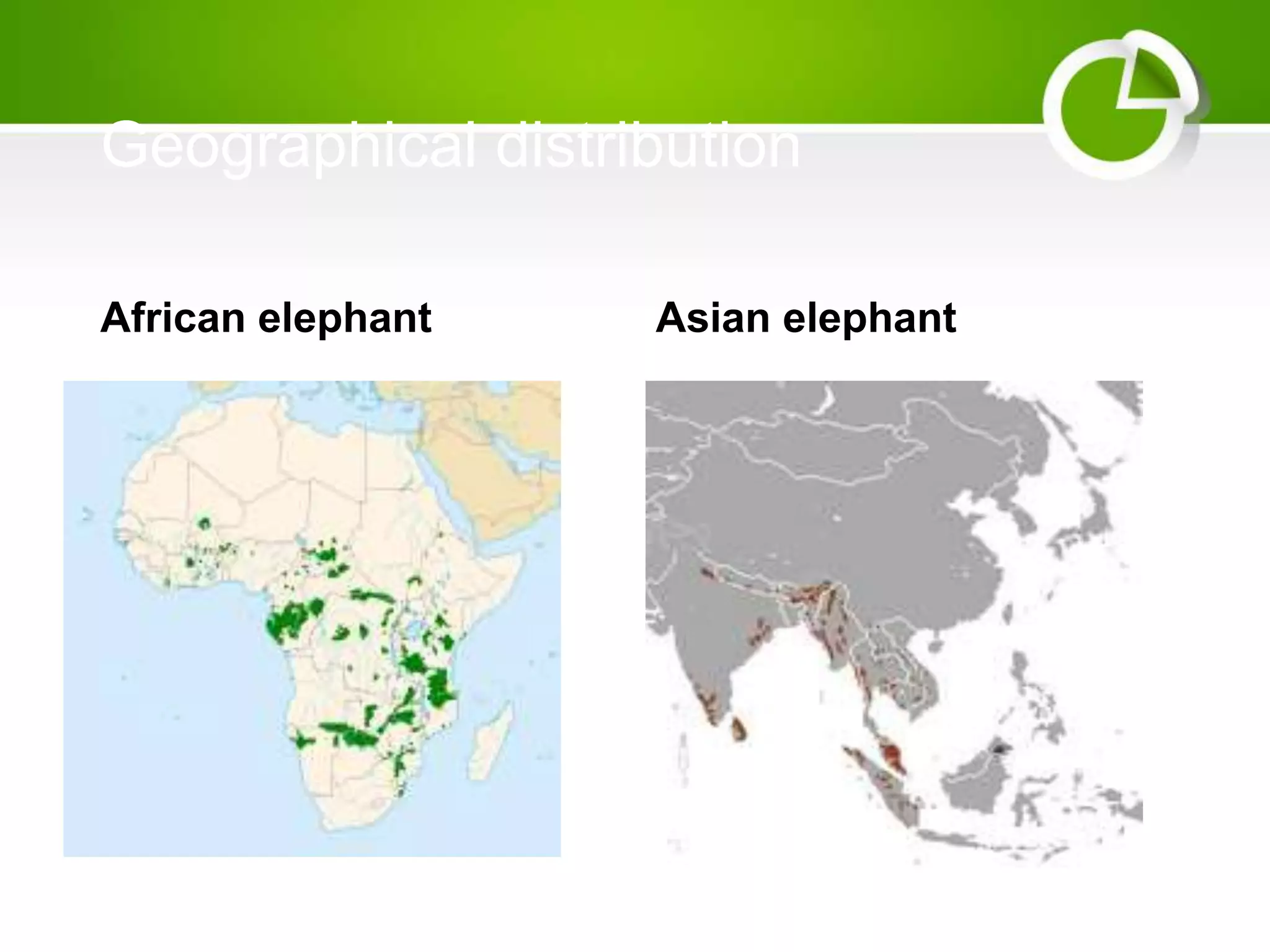
- Geographical distribution in Africa and Asia, and habitats in forests, grasslands, and scrublands.
- Diet of 140-270 kg of plants per day and 140-200 liters of water.
- Biological features like their size, lifespan, gestation period, and temperature regulation.
- Social behaviors and communication via sounds and body language.
- Relationship with humans as work animals, entertainment, economic value, and pets.
- Differences between Asian and African elephants.
- Common diseases like anthrax, tuberculosis, and parasites.
- Restraining techniques