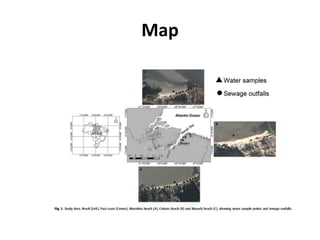
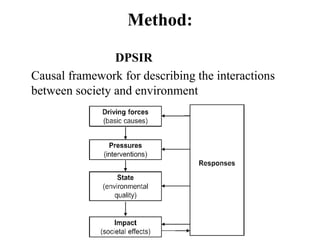
The presentation discusses the Amazon coastal area, focusing on the environmental study of its mangrove forests and recreational beaches affected by human activity and natural processes. It employs the DPSIR framework to analyze drivers, pressures, states, impacts, and responses regarding beach management and environmental conditions. The conclusion highlights the lack of local authority response and recommends measures such as improved planning, environmental monitoring, and sewage management.