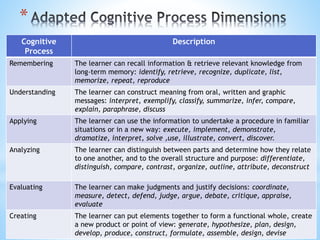
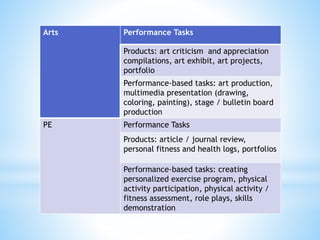
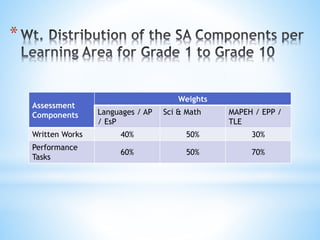
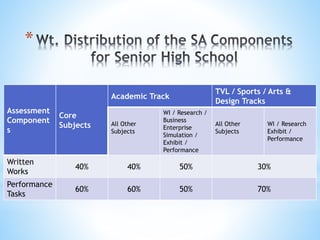
The document outlines a comprehensive approach to assessment that emphasizes holistic and authentic evaluation of student learning, prioritizing formative assessments to inform teaching and promote student growth. It details various assessment strategies, including written works and performance tasks, requiring teacher flexibility and collaboration with students and parents for effective feedback and remediation. The document also specifies guidelines for grading, ensuring that assessment methods are fair, reliable, and aligned with essential learning competencies.