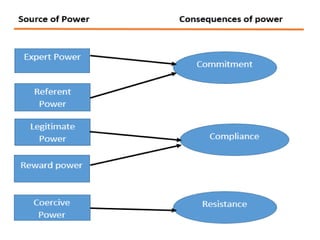
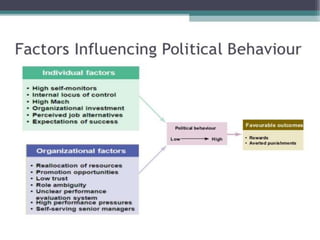
This document discusses power and politics in organizations. It defines power as one's ability to influence others, and notes that power comes from formal positions or informal personal characteristics. There are nine tactics people use to influence others, such as rational persuasion, inspiration appeals, or pressure. Individual factors like personality and job outlook influence political behavior. Organizational factors like ambiguous roles, performance pressures, and self-serving managers can also encourage politics in the workplace.