1. Retinal prostheses aim to restore vision for those with retinal dystrophies like retinitis pigmentosa which destroy photoreceptors. They work by using a camera to capture images and then stimulating remaining inner retinal cells or ganglion cells with electrodes to generate visual perceptions.
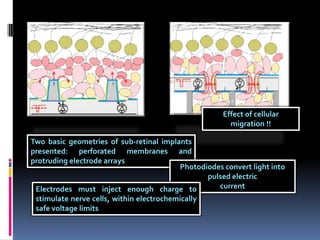
2. Two types of implants exist - epiretinal which sit on top of the retina and subretinal underneath. Issues include biocompatibility and stability of electrode materials over long periods.
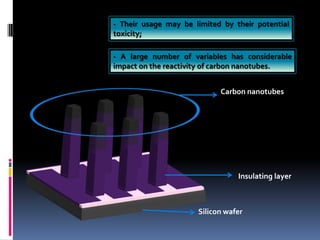
3. Carbon nanotubes show potential as an electrode material as they are biocompatible, robust, and flexible with superior electrochemical properties for long-term stimulation. However, their toxicity is a concern requiring further