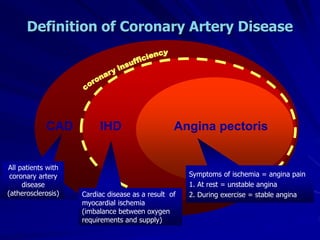
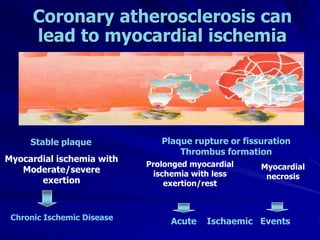
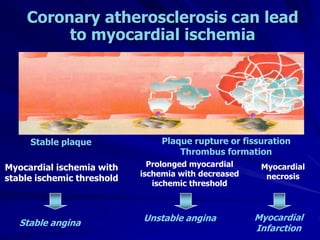
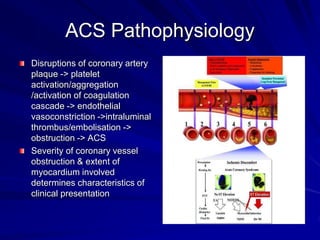
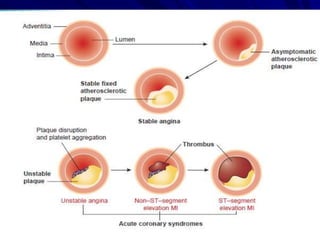
1) Ischaemic heart disease (IHD) results from a lack of oxygen supply to the heart muscle due to narrowed coronary arteries. It presents as stable angina, unstable angina, or myocardial infarction.
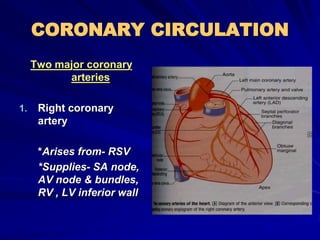
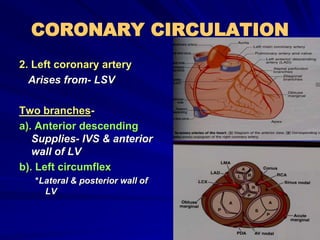
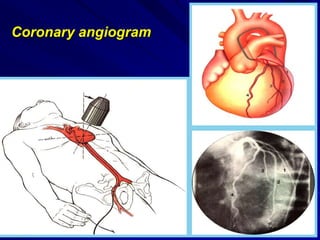
2) Coronary arteries supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. Blockages in these arteries due to atherosclerosis can cause angina or infarction depending on the severity and location of the blockage.
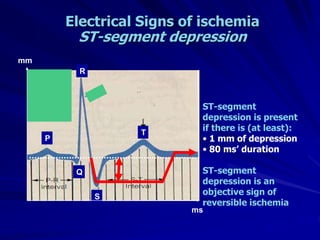
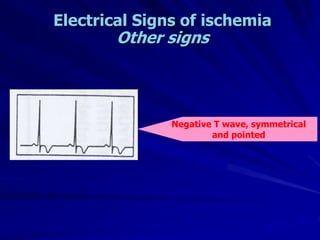
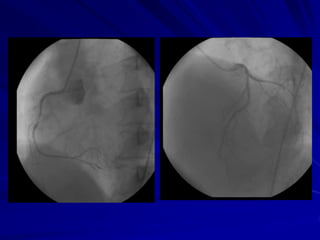
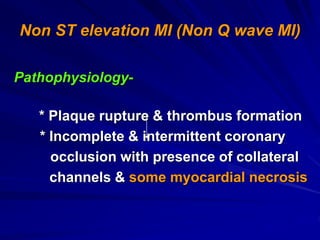
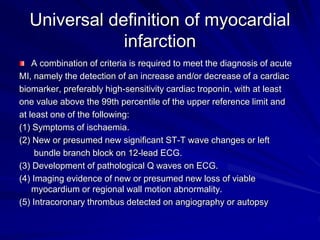
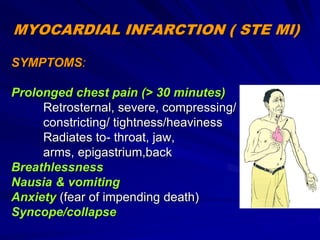
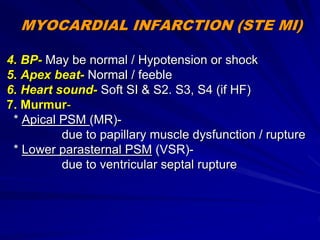
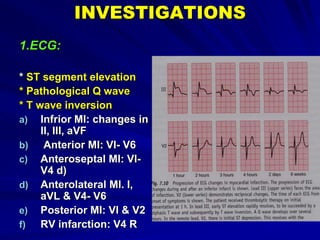
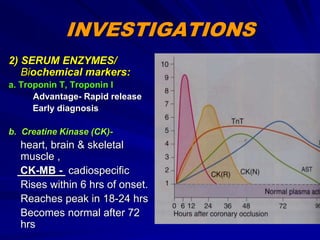
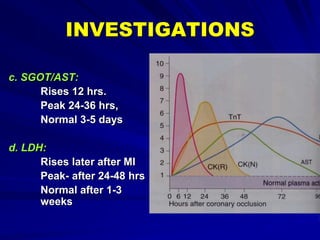
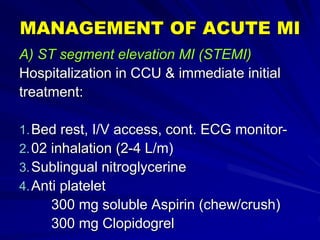
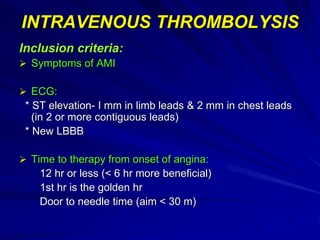
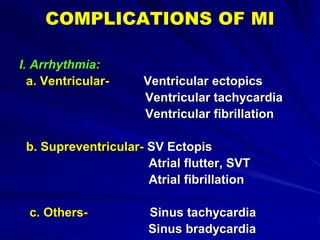
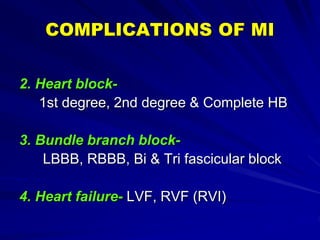
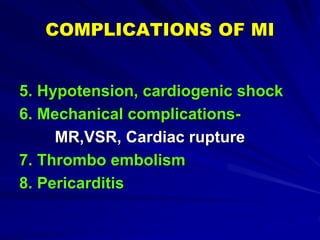
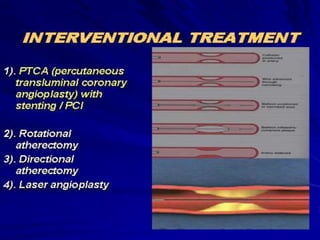
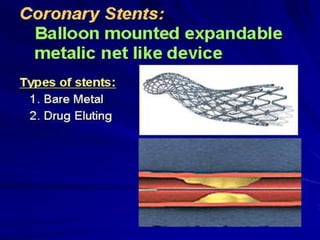
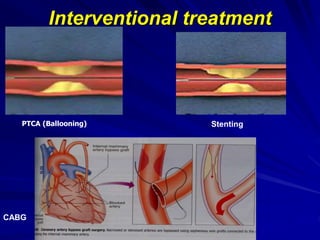
3) Myocardial infarction occurs when a blockage completely cuts off blood flow, causing death of heart muscle tissue. It is classified as non-ST elevation or ST-elevation MI depending on ECG findings. Treatment involves reperfusion through thrombolysis or angioplasty as well