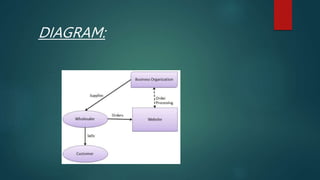
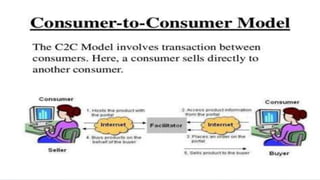
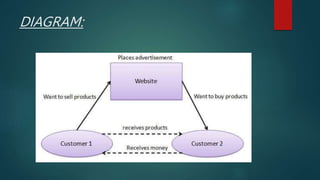
Digital marketing and e-commerce were defined. Digital marketing uses digital technologies like the internet and mobile phones to market products and services. E-commerce is buying and selling online. Benefits of digital marketing include connecting with mobile customers, using content online, tracking customers, analyzing data, and optimizing for conversion. E-commerce draws on technologies like mobile commerce and electronic funds transfer. It has impacted markets, retailers, customers, and employment. Forms of e-commerce include B2B, B2C, C2B, and C2C models. The UK had the highest per capita e-commerce spending, while the Czech Republic gets the biggest revenue contribution from online sales. Logistics in e-commerce concerns order






![BENEFITS OF IT:
Online shopping for retail sales direct to consumers via Web sites and mobile
apps, and conversational commerce via live chat, chatbots, and voice
assistants[3]
Providing or participating in online marketplaces, which process third-party
business-to-consumer or consumer-to-consumer sales
Business-to-business buying and selling;
Gathering and using demographic data through web contacts and social
media
Business-to-business (B2B) electronic data interchange
Marketing to prospective and established customers by e-mail or fax (for
example, with newsletters)
Engaging in pretail for launching new products and services
Online financial exchanges for currency exchanges or trading purposes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationdigitalmarketing-230301164150-3b4f337d/85/presentation-digital-marketing-pptx-7-320.jpg)
![FORMS :
Contemporary electronic commerce can be classified into two categories.
The first category is business based on types of goods sold (involves
everything from ordering "digital" content for immediate online
consumption, to ordering conventional goods and services, to "meta"
services to facilitate other types of electronic commerce). The second
category is based on the nature of the participant (B2B, B2C, C2B and
C2C);[37]
On the institutional level, big corporations and financial institutions use
the internet to exchange financial data to facilitate domestic and
international business. Data integrity and security are pressing issues for
electronic commerce.
Aside from traditional e-commerce, the terms m-Commerce (mobile
commerce) as well (around 2013) t-Commerce[38] have also been used.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationdigitalmarketing-230301164150-3b4f337d/85/presentation-digital-marketing-pptx-8-320.jpg)
![Global trends :
In 2010, the United Kingdom had the highest per capita e-commerce
spending in the world.[39] As of 2013, the Czech Republic was the European
country where e-commerce delivers the biggest contribution to the
enterprises´ total revenue. Almost a quarter (24%) of the country's total
turnover is generated via the online channel.[40]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationdigitalmarketing-230301164150-3b4f337d/85/presentation-digital-marketing-pptx-9-320.jpg)