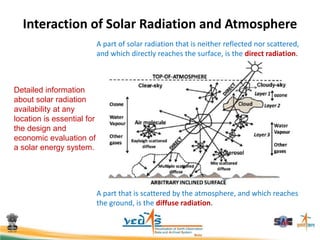
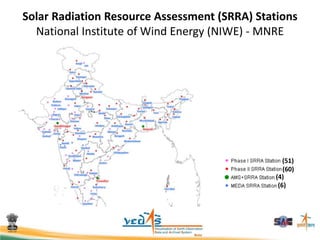
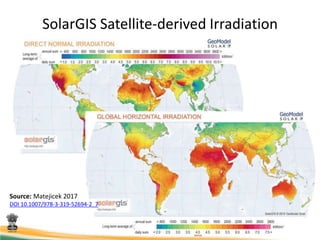
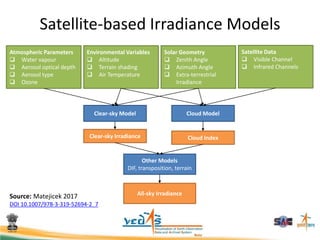
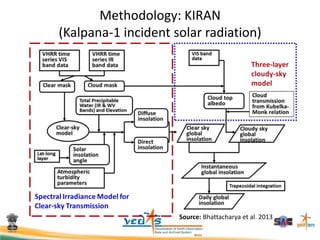
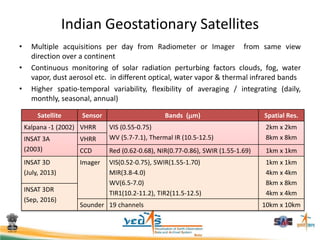
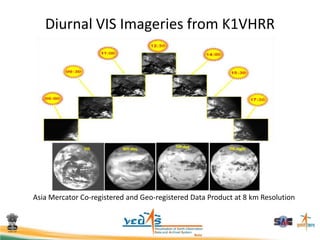
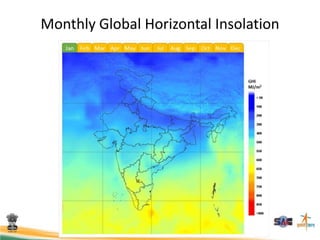
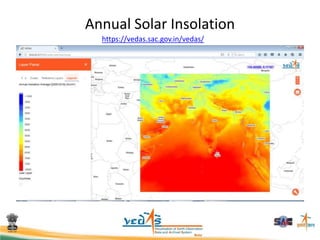
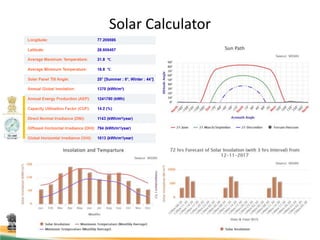
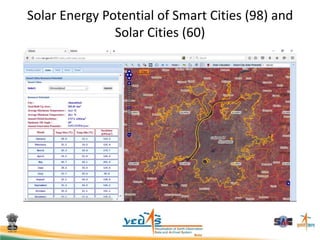
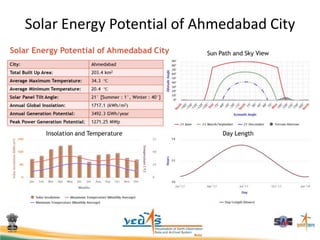
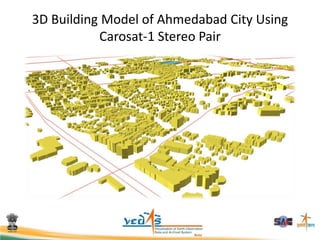
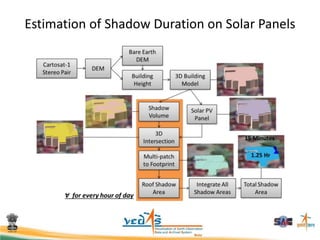
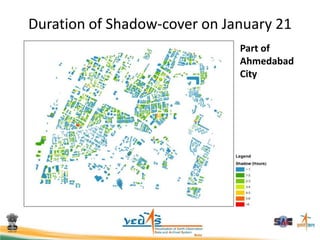
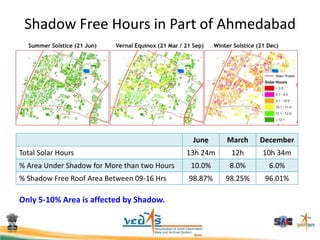
This document discusses using satellite data to assess solar energy potential in India. It describes how satellites can monitor factors like clouds and aerosols to model solar irradiance. The KIRAN methodology uses geostationary satellites to generate diurnal and monthly solar insolation maps of India at high spatial resolution. Tools have been developed like a solar calculator app and an online database to estimate roof-top solar potential in cities. Analysis of satellite stereo imagery can also estimate shadow effects on roofs. The work aims to help plan and evaluate solar energy projects across India.