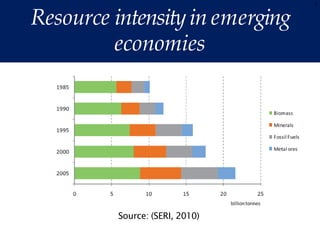
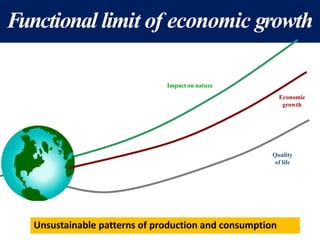
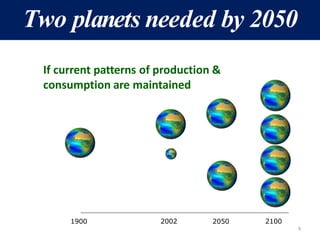
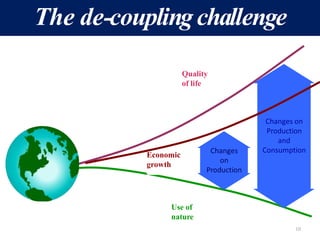
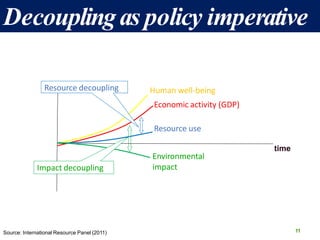
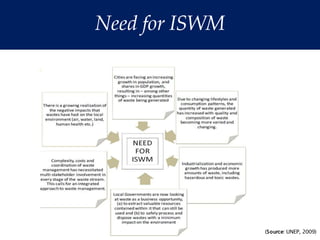
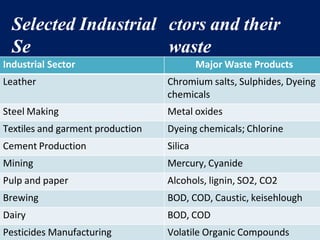
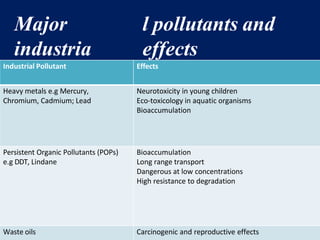
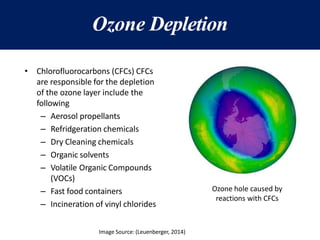
The document discusses the urgent need for sustainable development to address the environmental challenges posed by industrial growth and increasing consumption, which threaten future generations. It highlights the concept of resource decoupling, emphasizing the necessity for industries to adopt sustainable practices and reduce their environmental impact. Additionally, it outlines the global sustainability goals established during various summits aimed at achieving socio-economic development while preserving ecosystems.