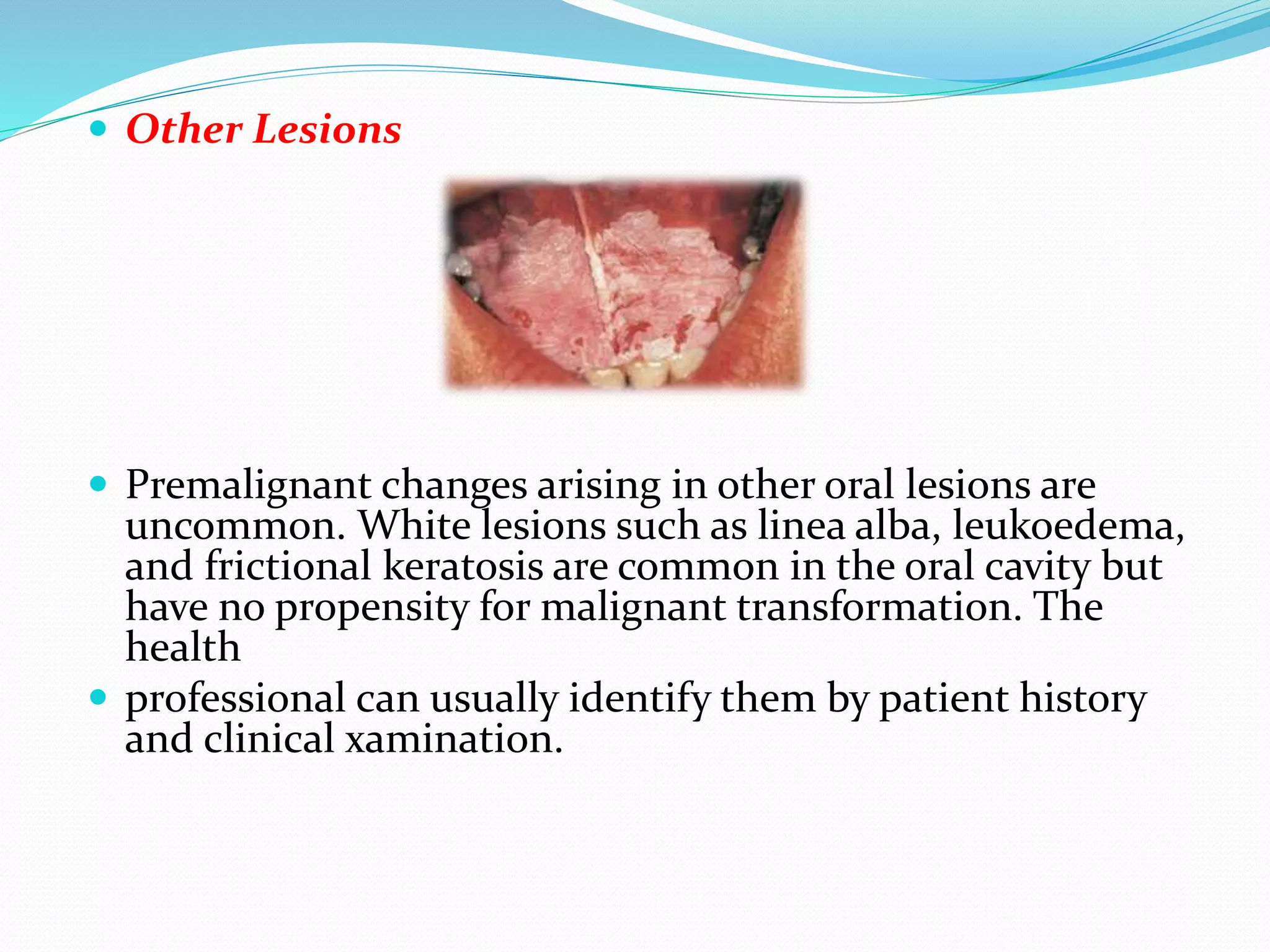
This document discusses clinical features that can indicate oral premalignancy. It begins by stating that clinical classification of oral lesions is difficult and subjective, while histopathology is more accurate for determining premalignant change. Leukoplakia and erythroplakia are two clinical lesions often considered premalignant, though leukoplakia has a low risk while erythroplakia has a high (91%) risk of dysplasia or malignancy. A biopsy should be considered for any persistent mucosal lesion to determine premalignant changes. Common sites of oral premalignancy are the buccal mucosa, palate, and floor of the mouth in individuals aged 50-69. Surgical