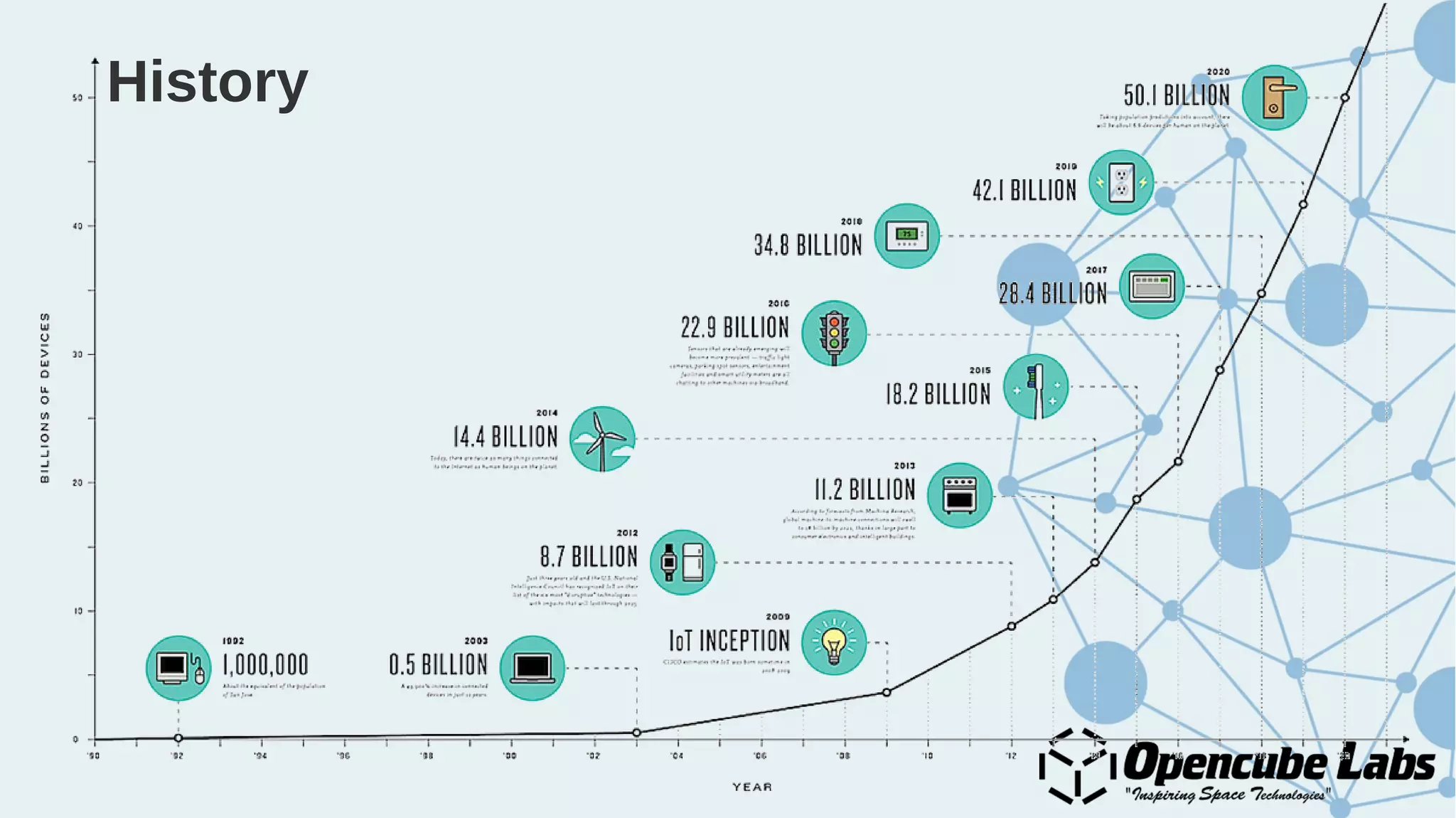
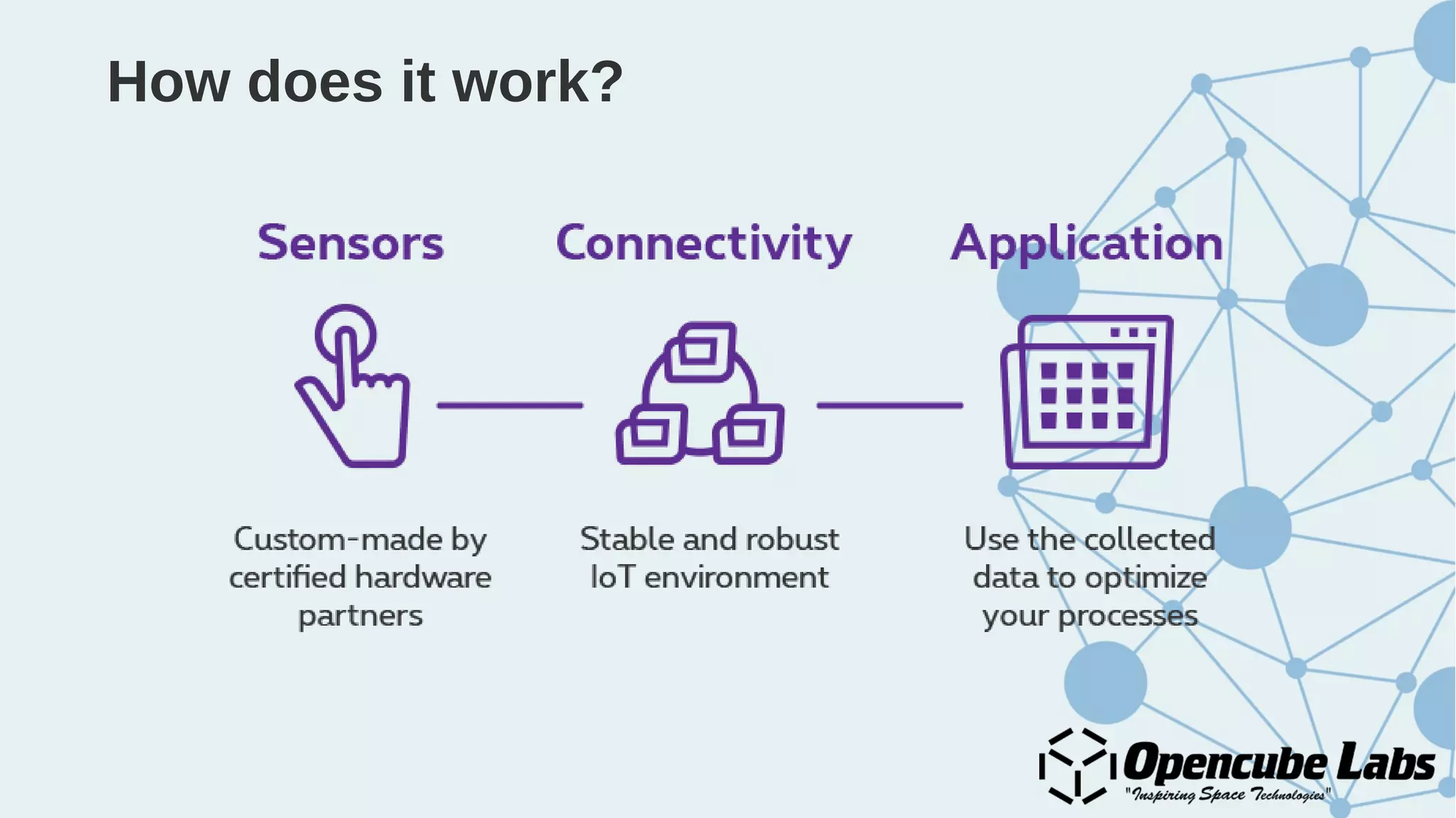
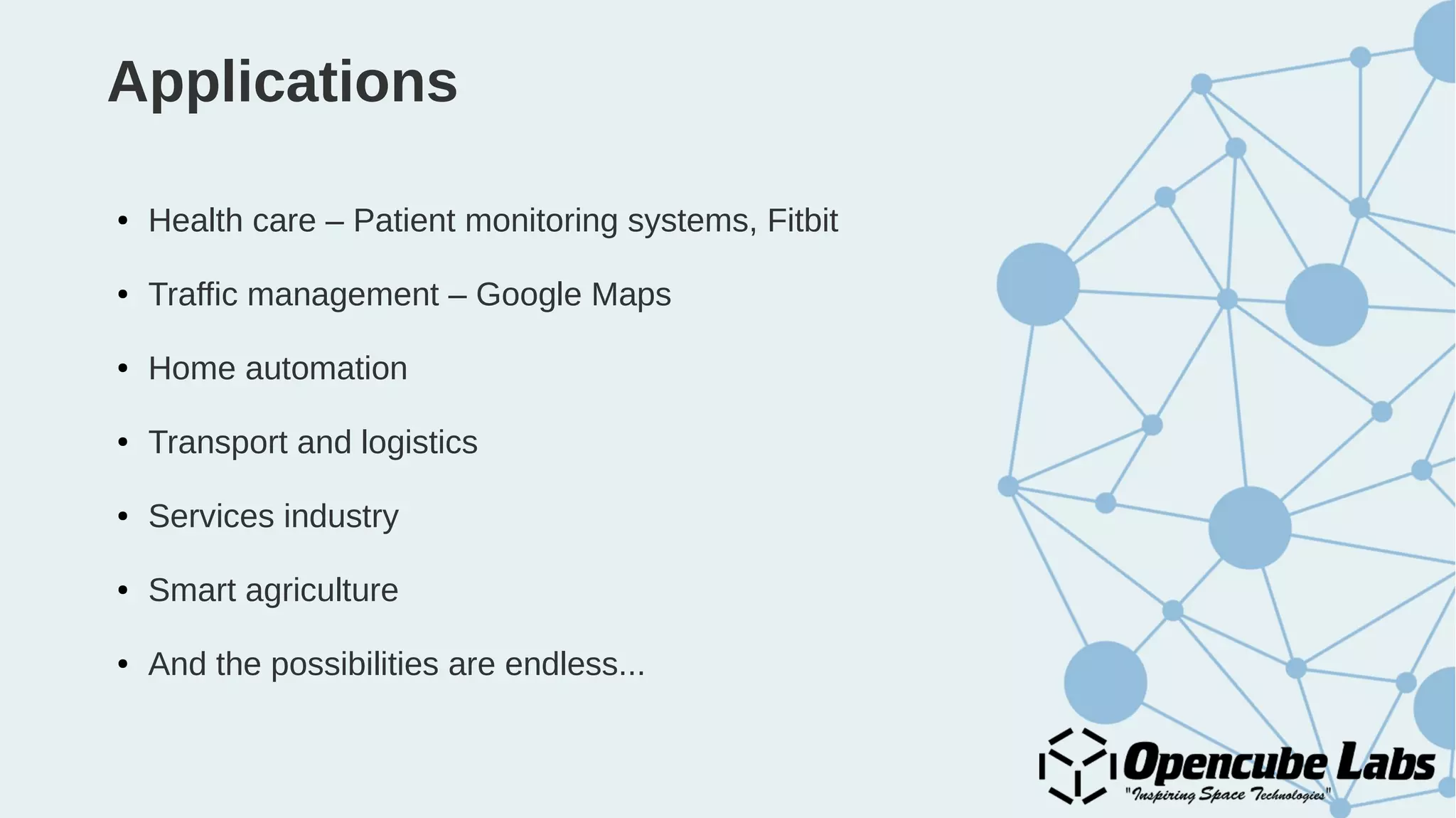
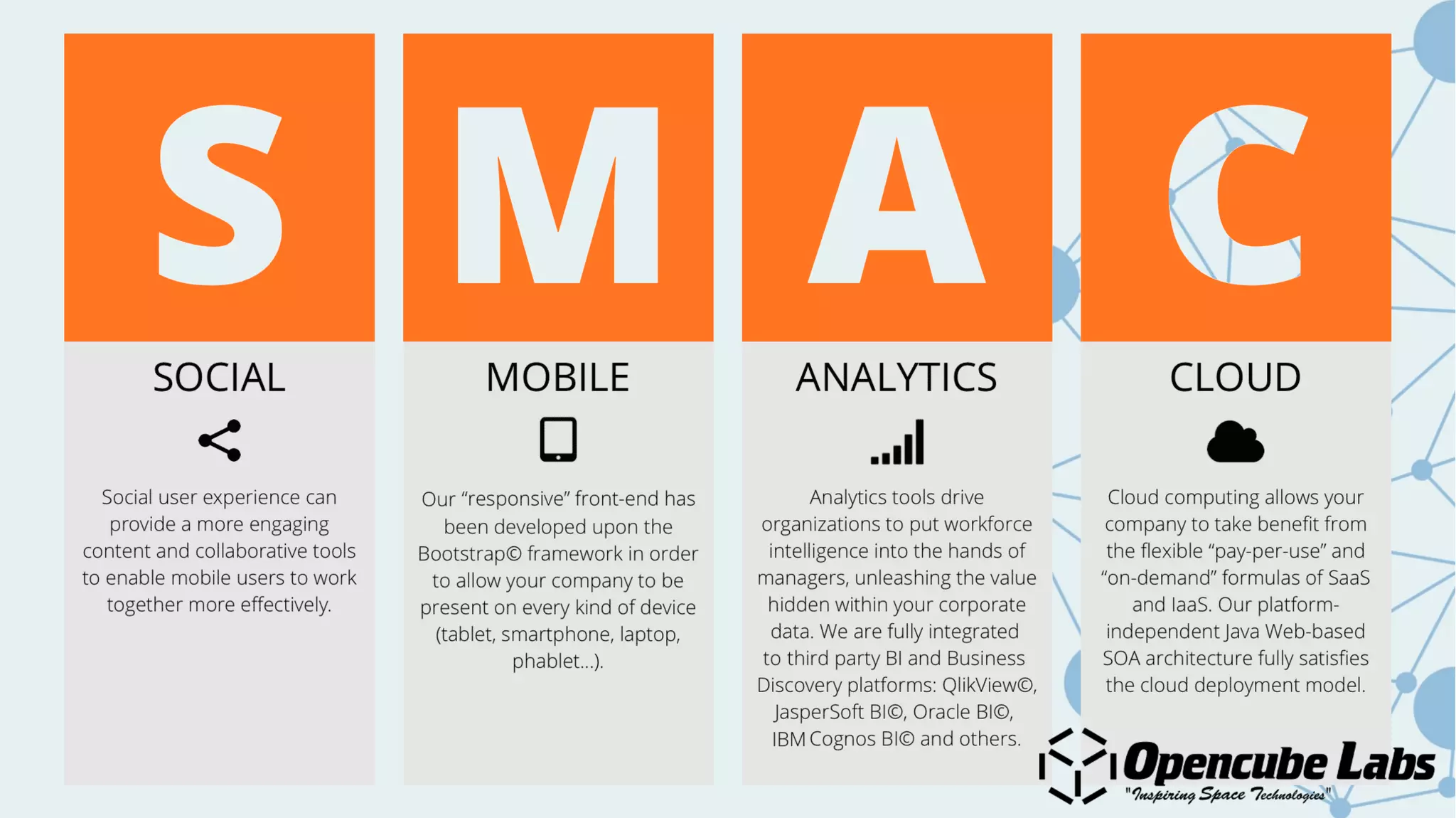
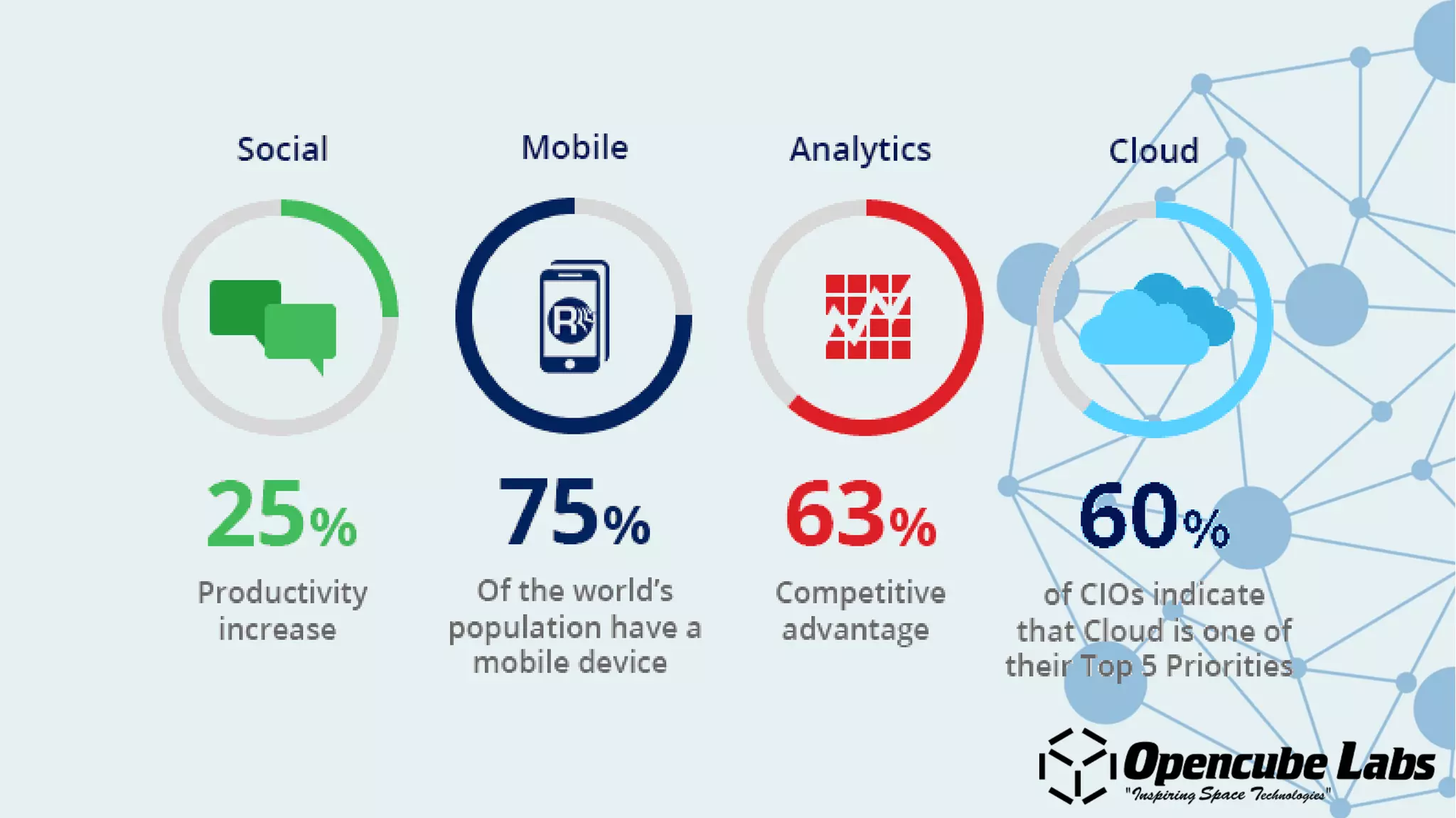
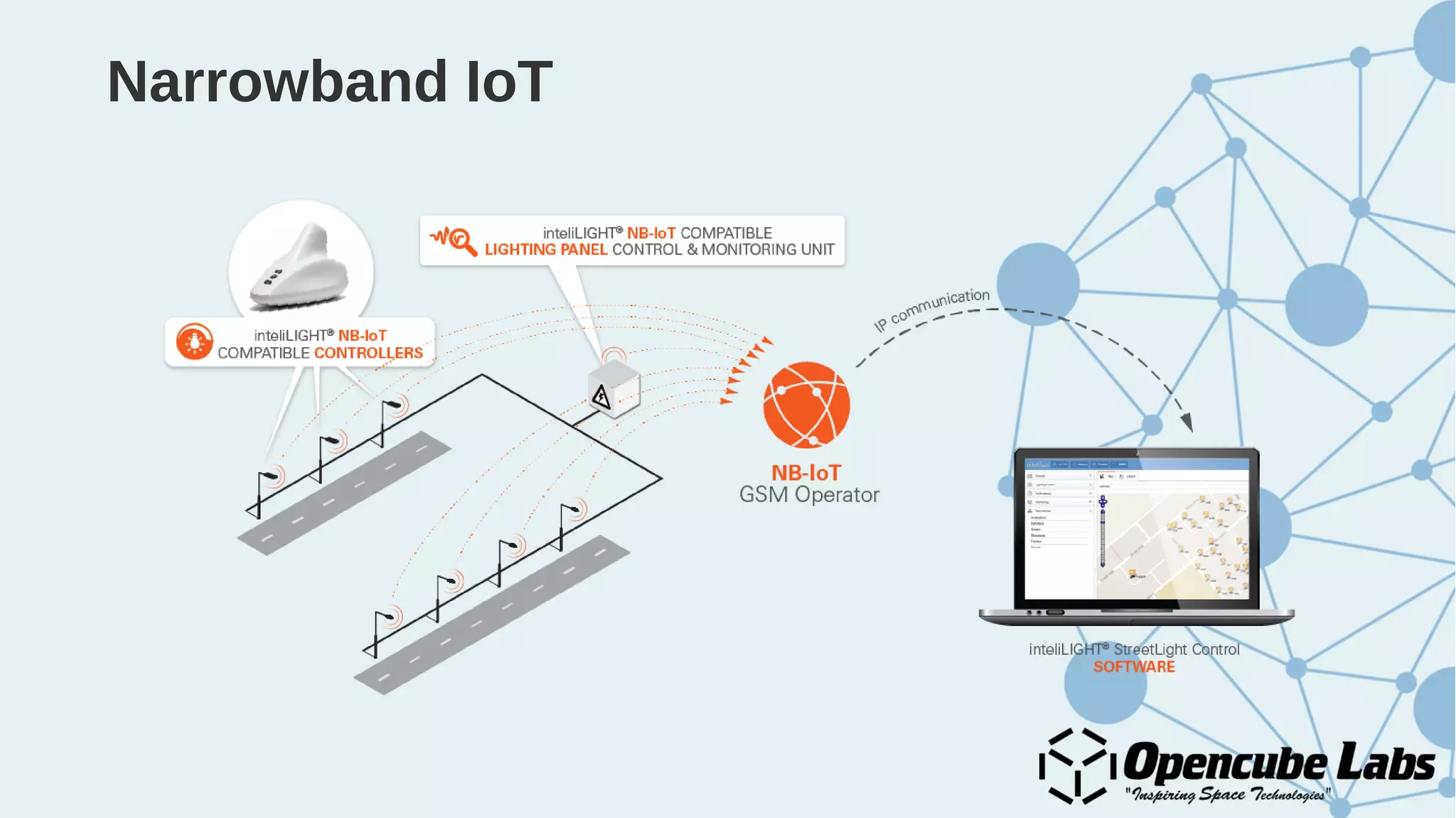
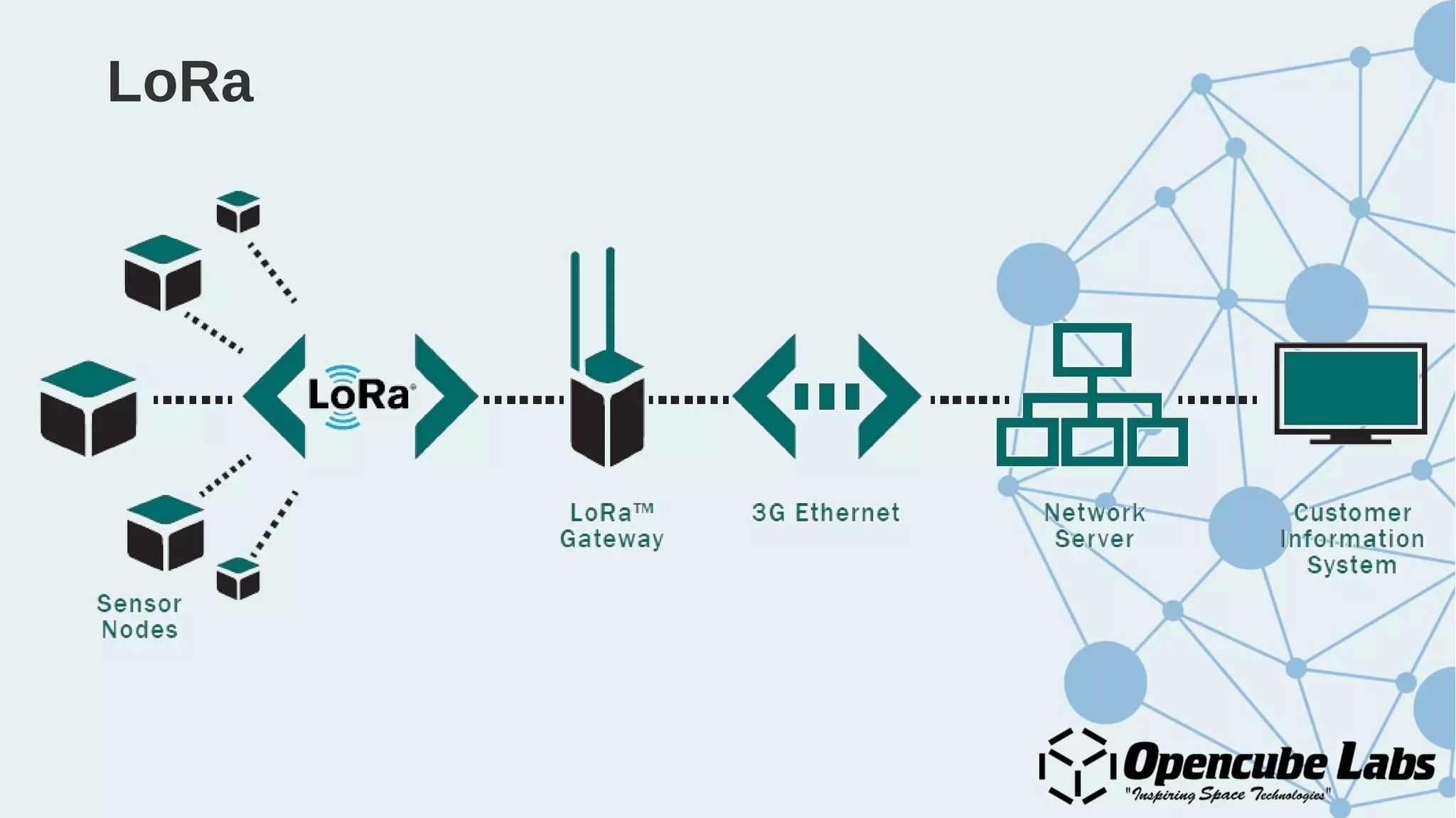
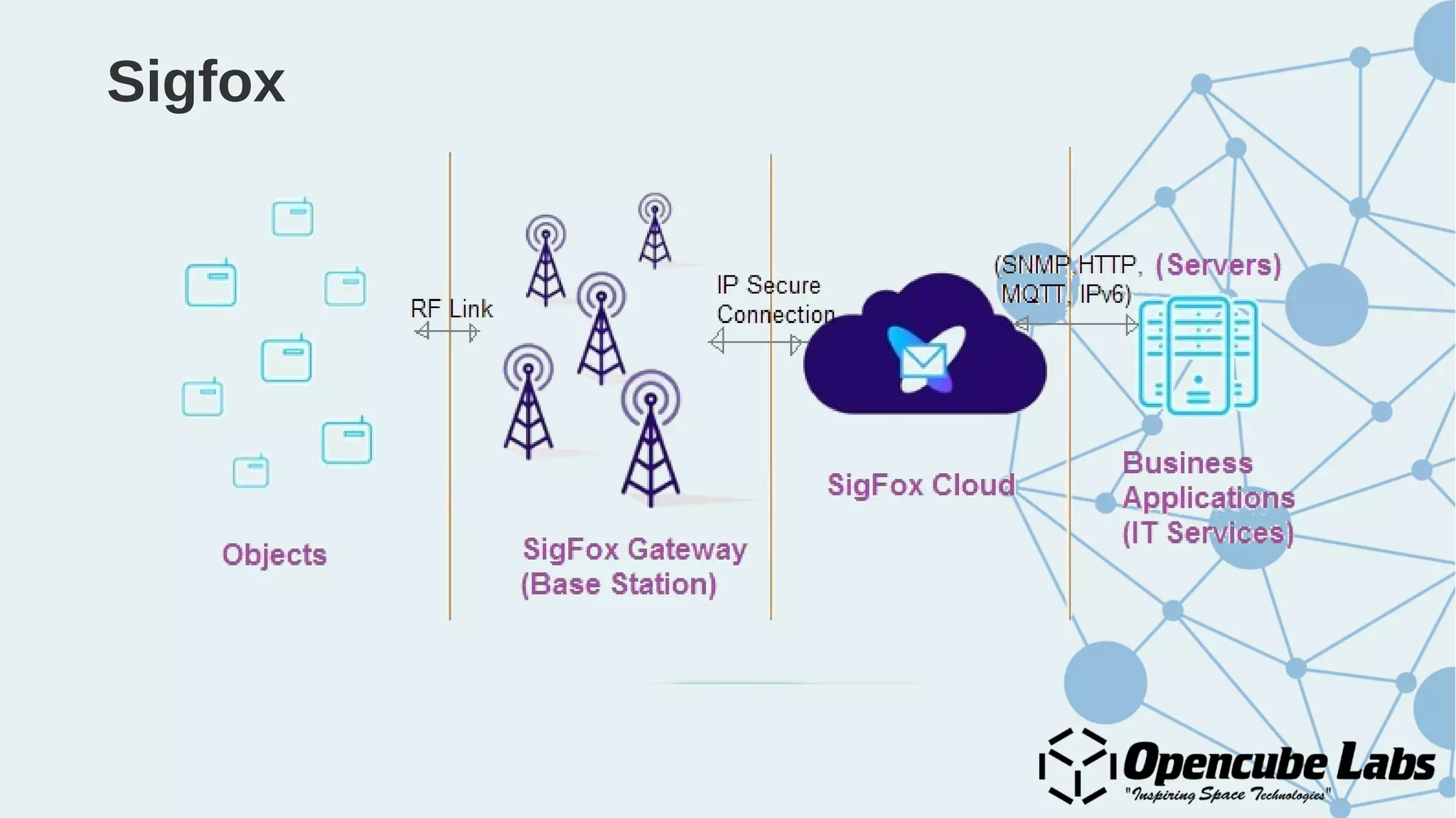
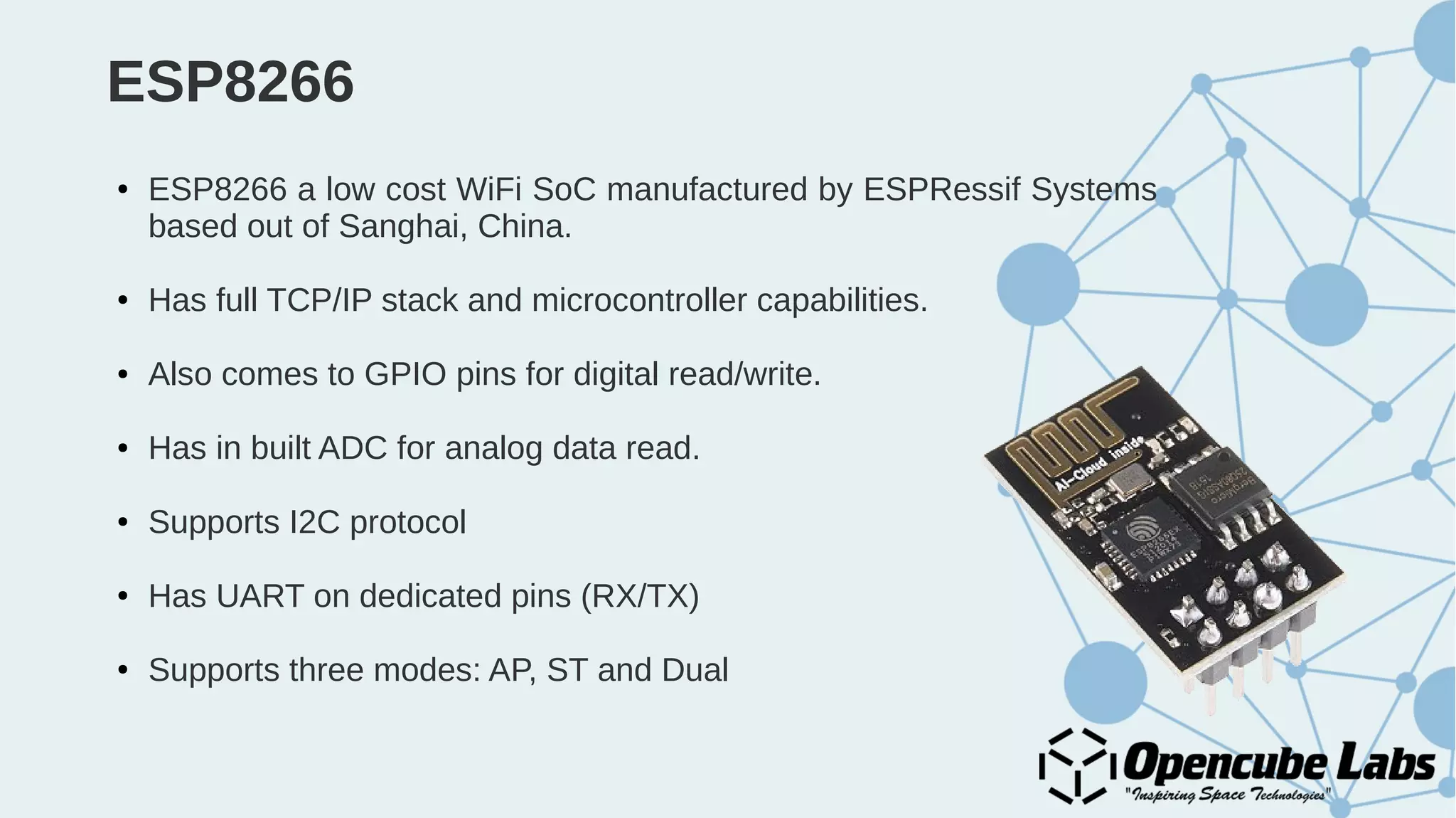
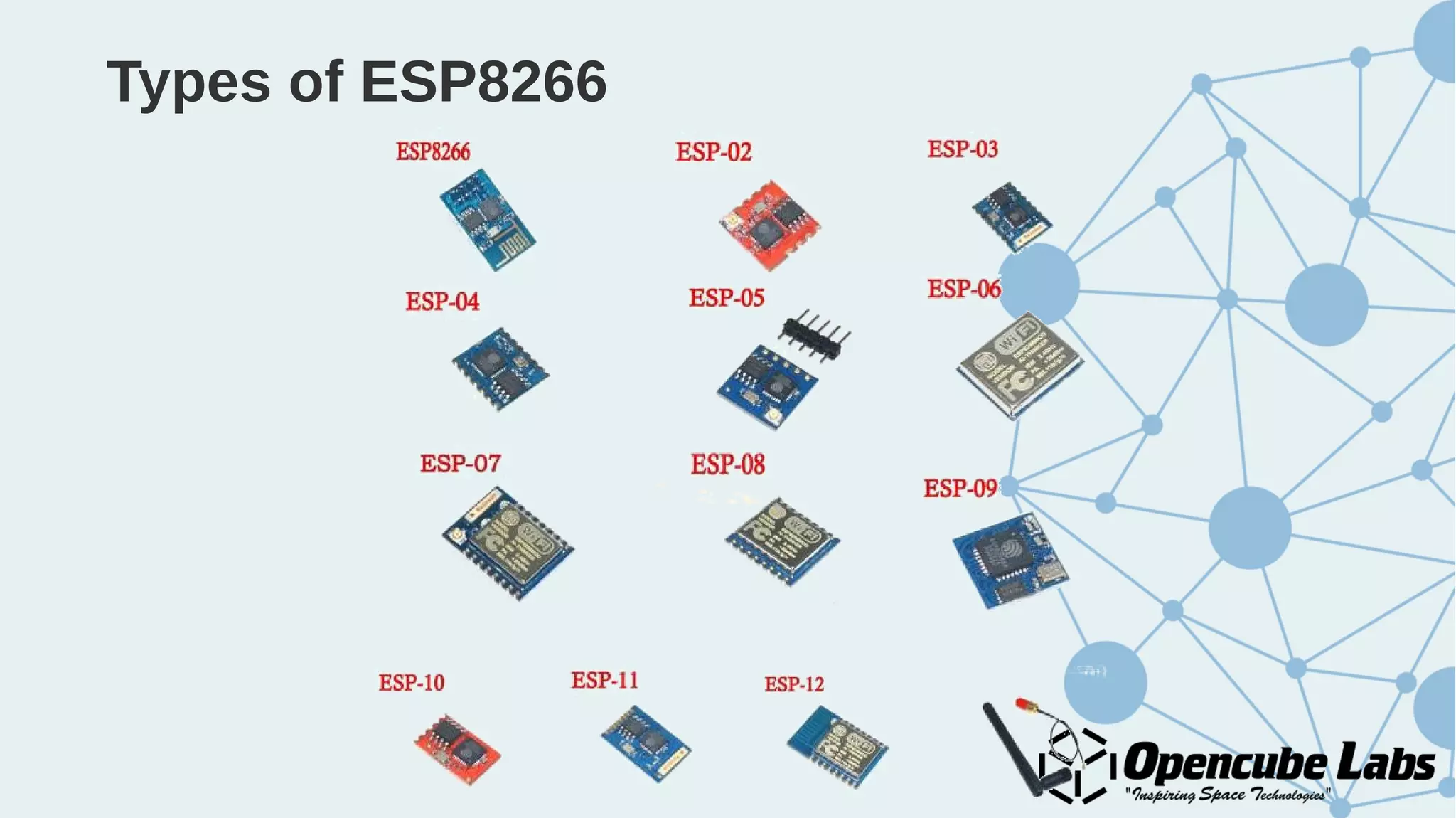
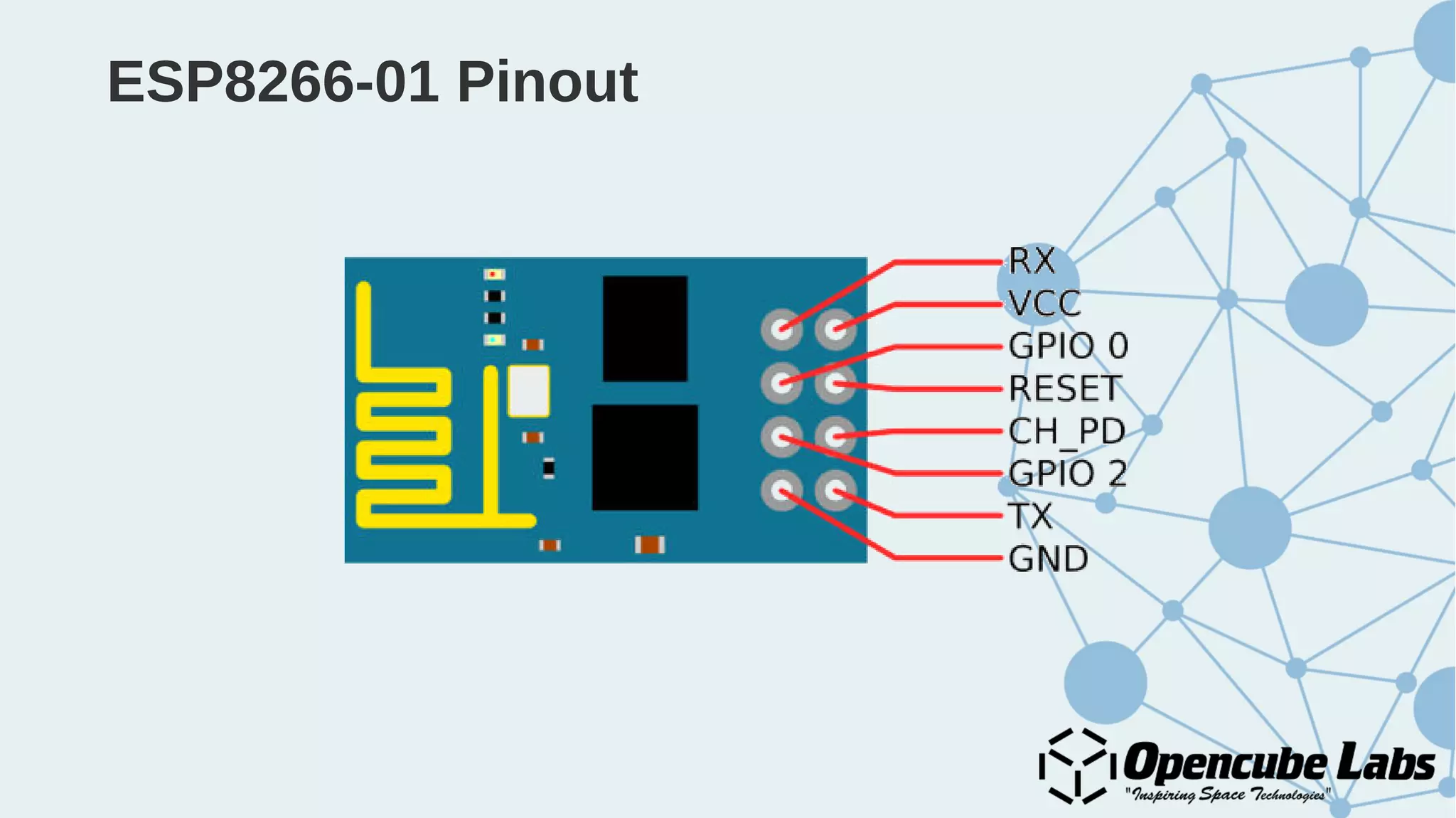
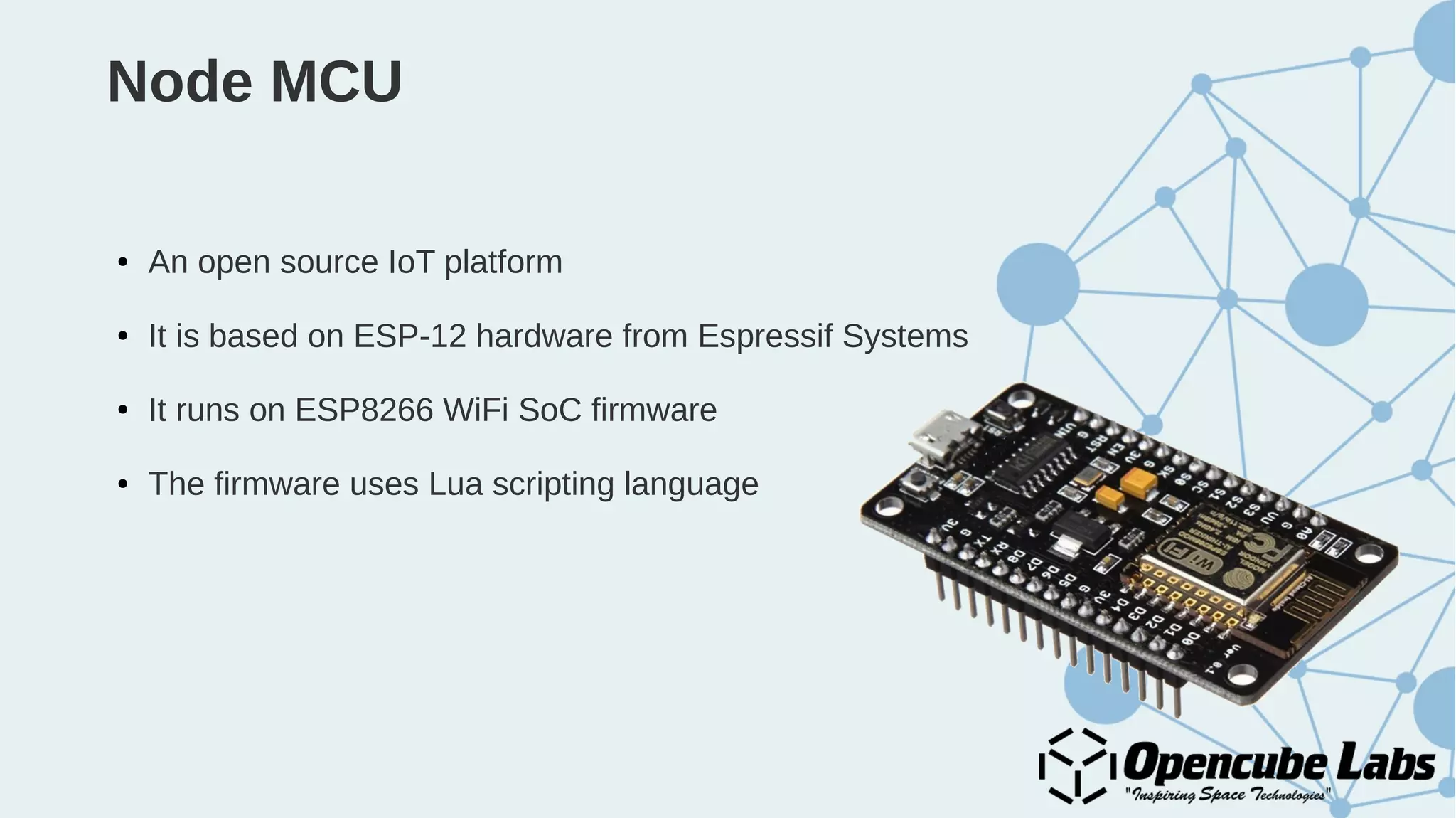
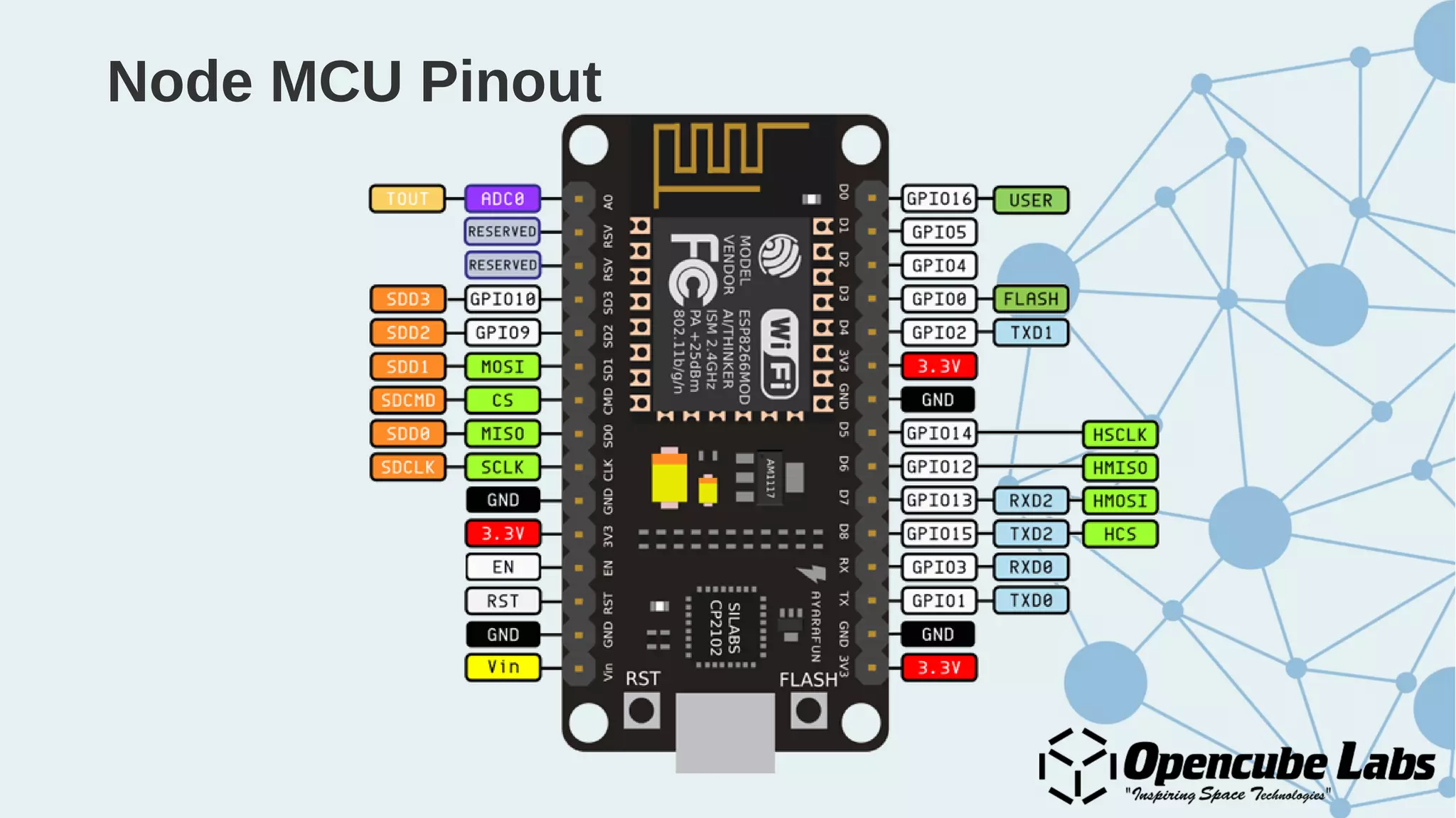
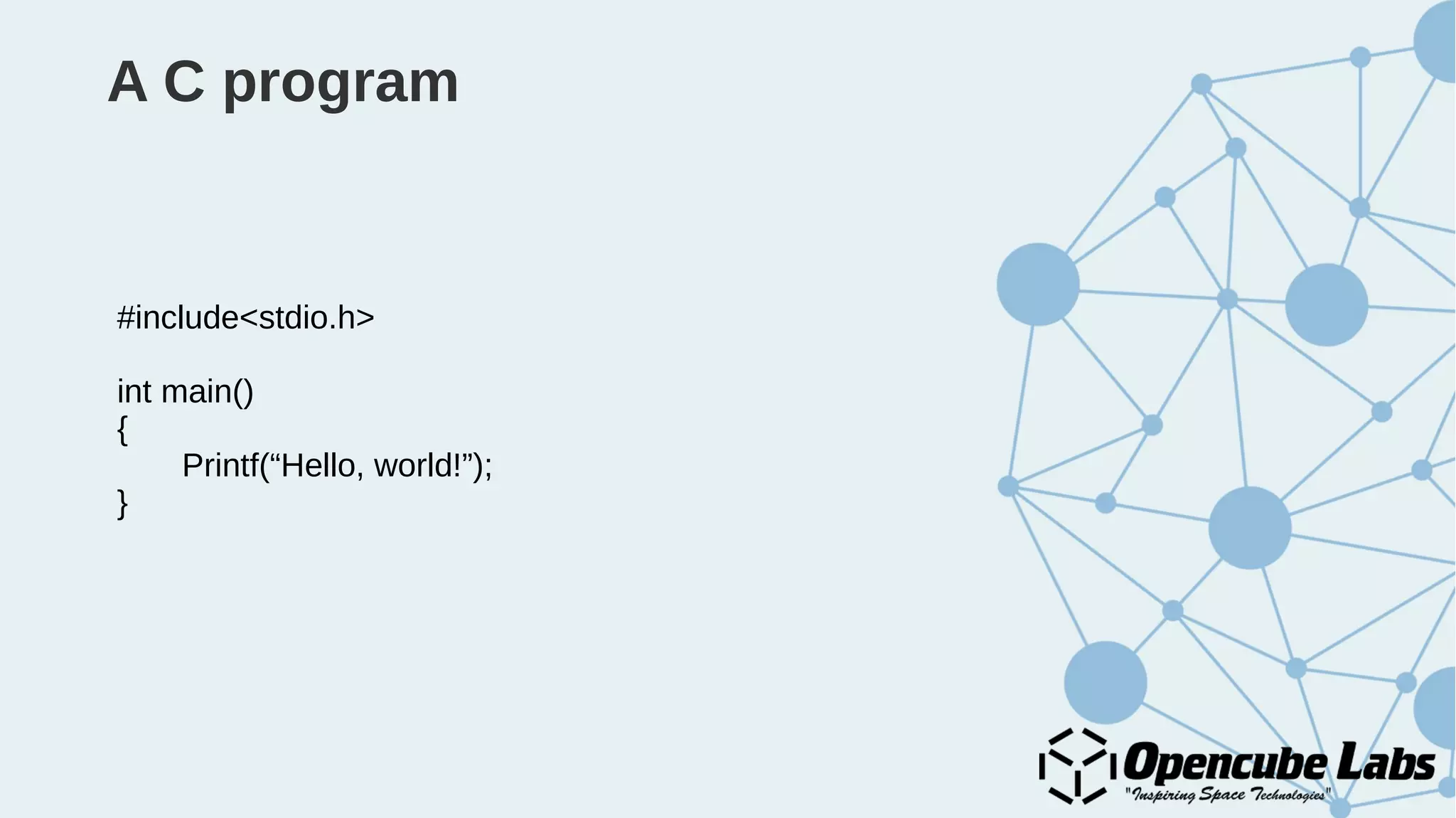
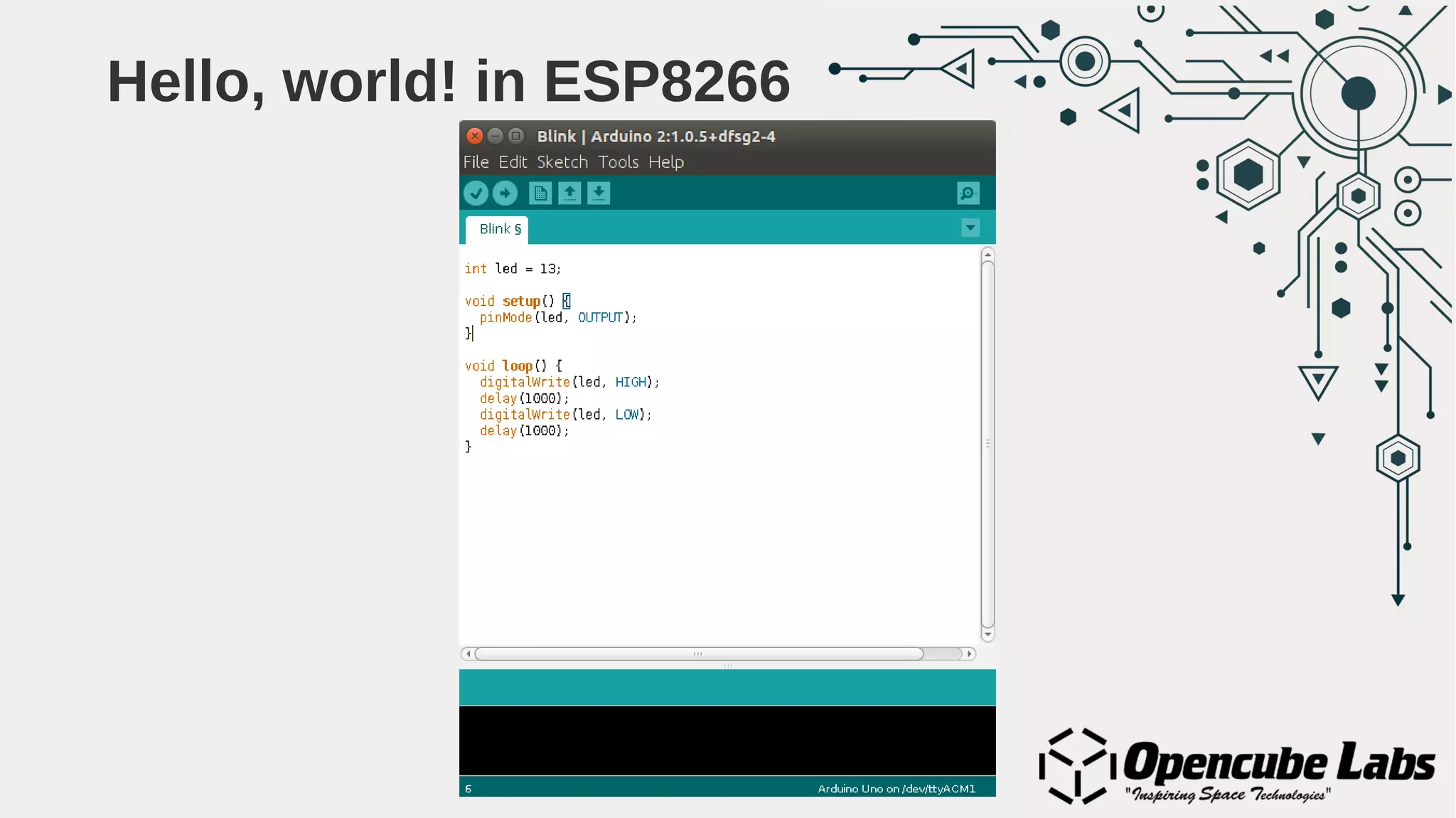
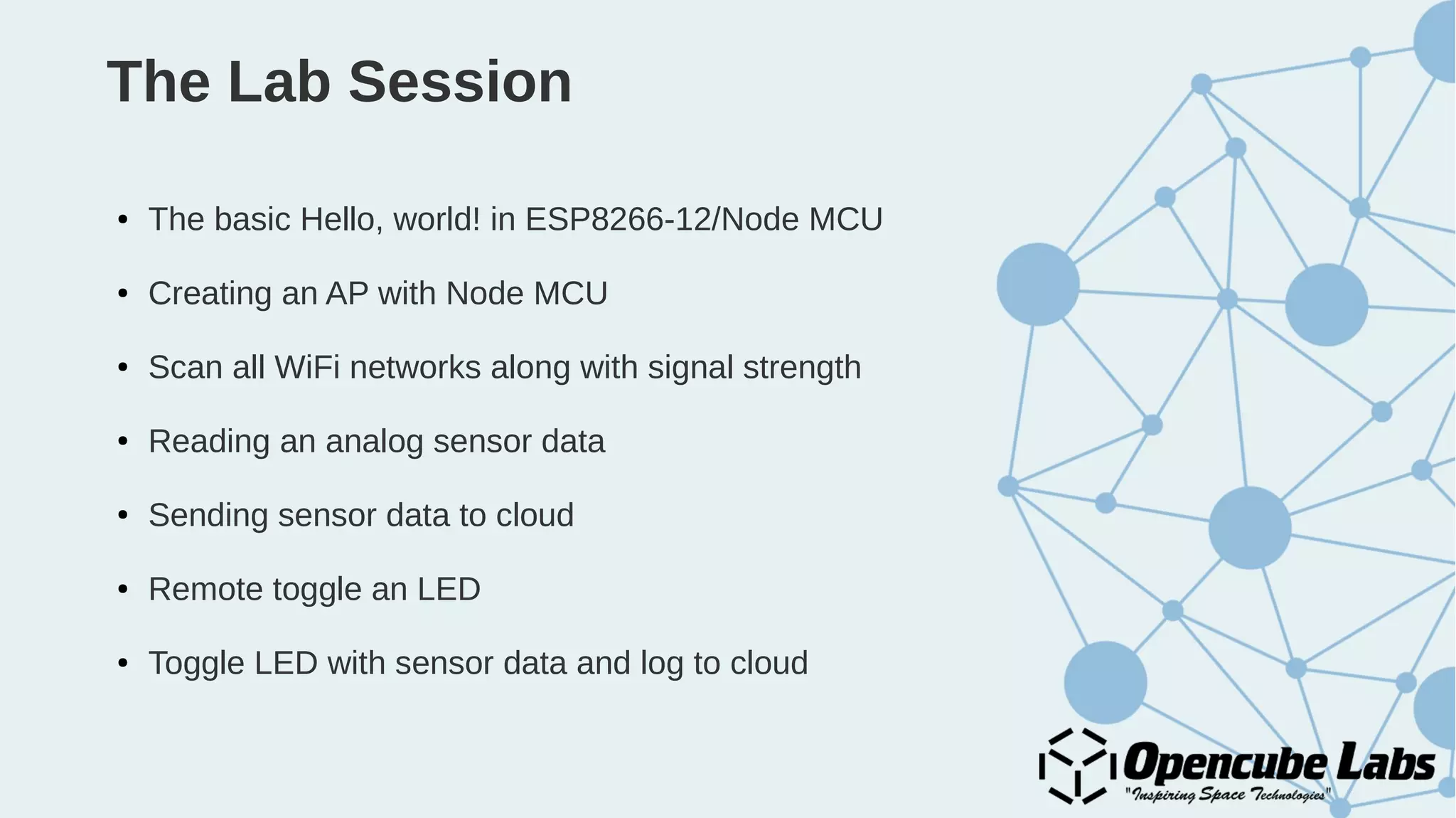
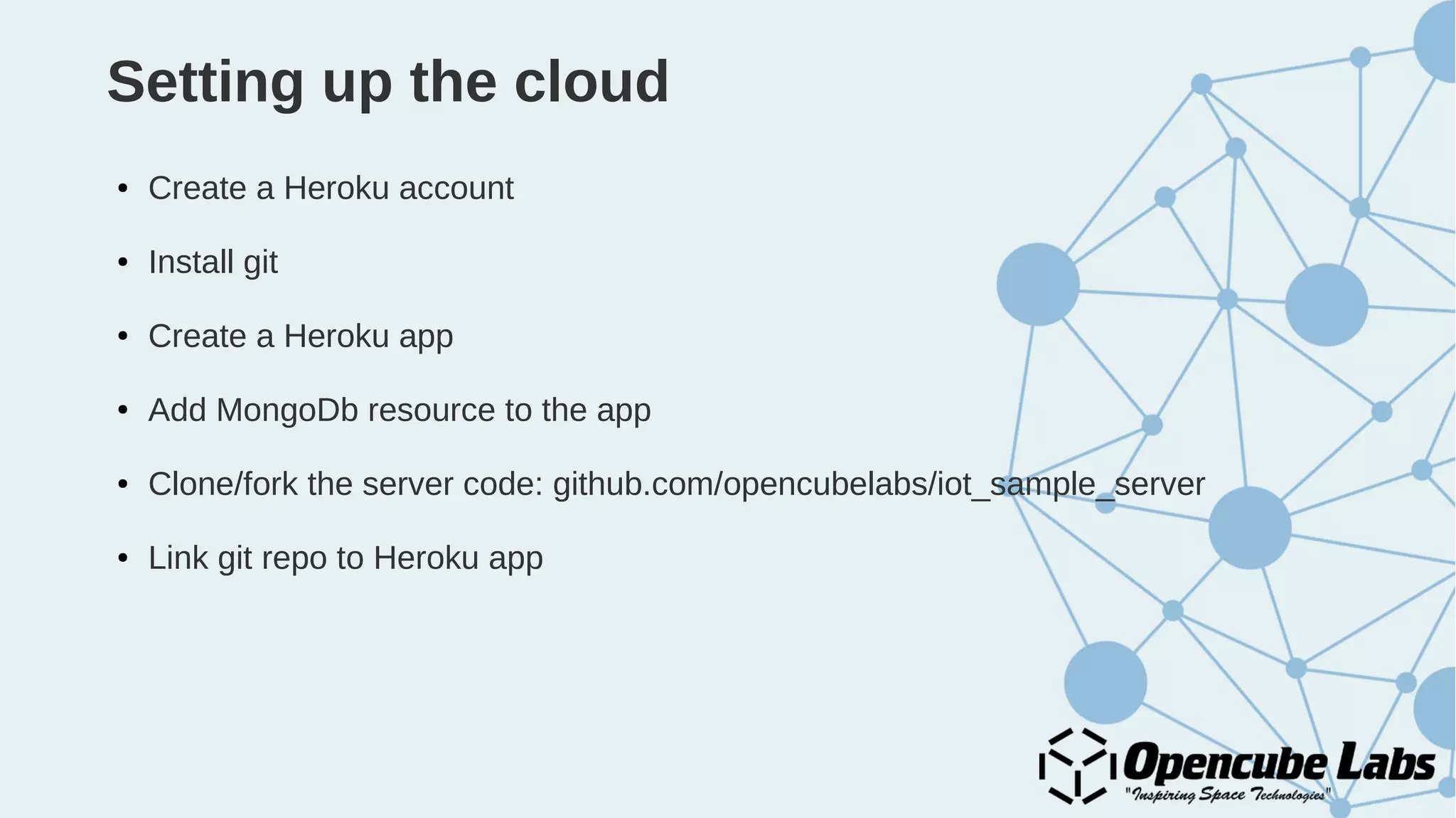
The document provides an overview of the Internet of Things (IoT), detailing its history, benefits, and various applications, including healthcare, traffic management, and smart agriculture. It emphasizes the use of the ESP8266 WiFi system-on-chip, along with programming practices, particularly using the Arduino IDE and NodeMCU platform. Additionally, it discusses setting up an IoT environment, encompassing cloud services and coding examples for sensor data management.