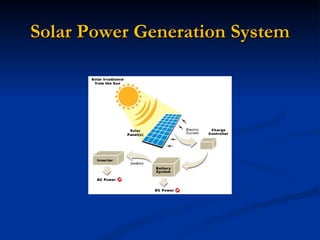
The document discusses solar power generation, distribution, and storage from small-scale solar power systems. It describes how solar power works by converting sunlight to electricity through photovoltaic cells or concentrating solar power systems. The document outlines the components of a solar power generation system and discusses photovoltaic effect. It also addresses performance factors, applications, advantages and disadvantages of solar power.