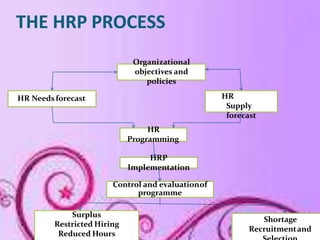
This document discusses human resource planning, including its definition, objectives, importance, process, and techniques. It defines HRP as balancing required and acquired human resources to meet organizational objectives. The key aspects covered are:
- HRP includes forecasting demand and supply of employees, identifying surpluses or shortages, and addressing them through actions like recruitment or redundancy.
- Factors like organizational growth, environment, and technology impact HRP. Techniques used include managerial judgment, ratio analysis, and mathematical models.
- Labour market analysis studies supply and demand forces for different jobs. Inventorying methods identify employee characteristics and capabilities.