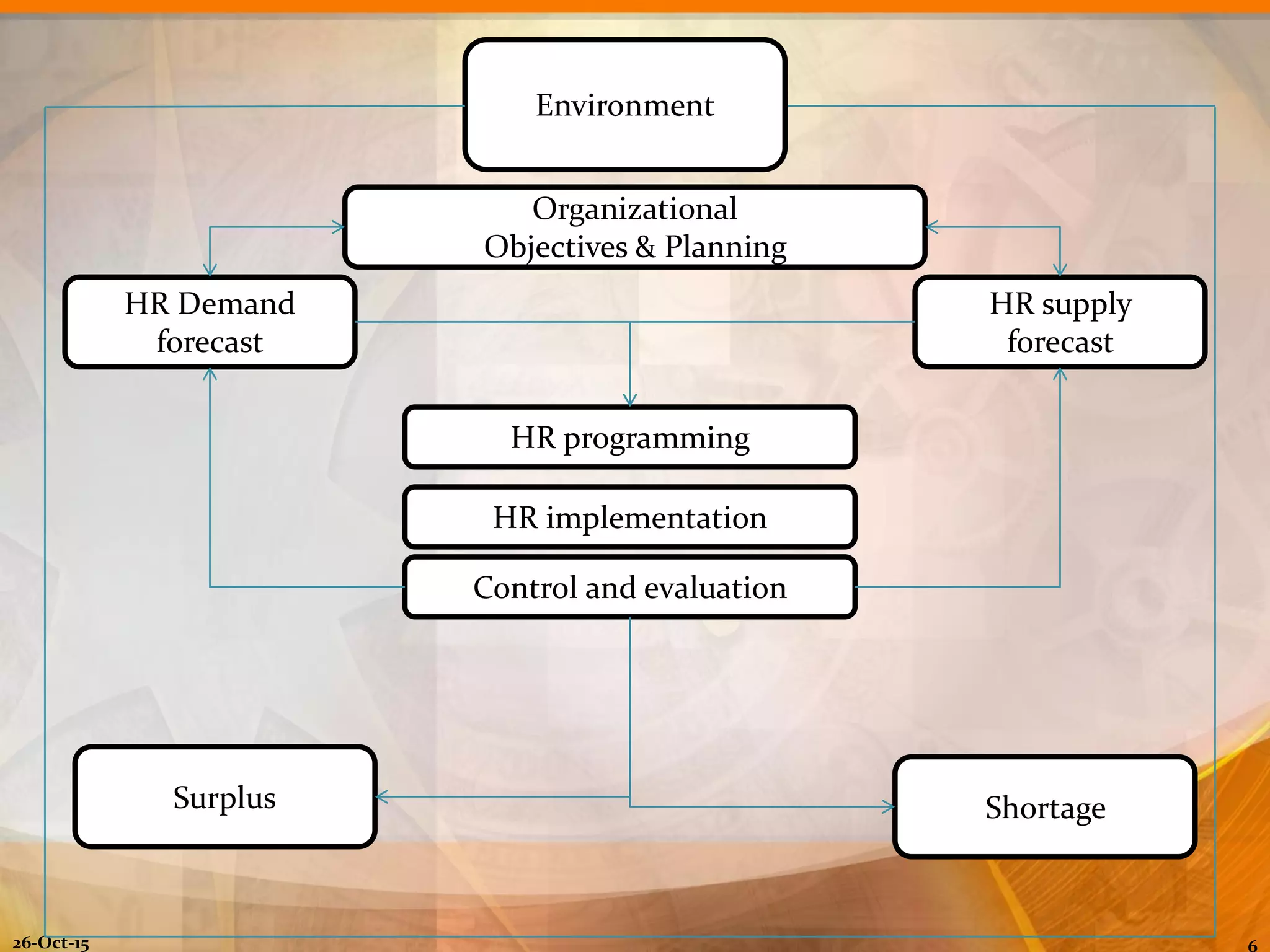
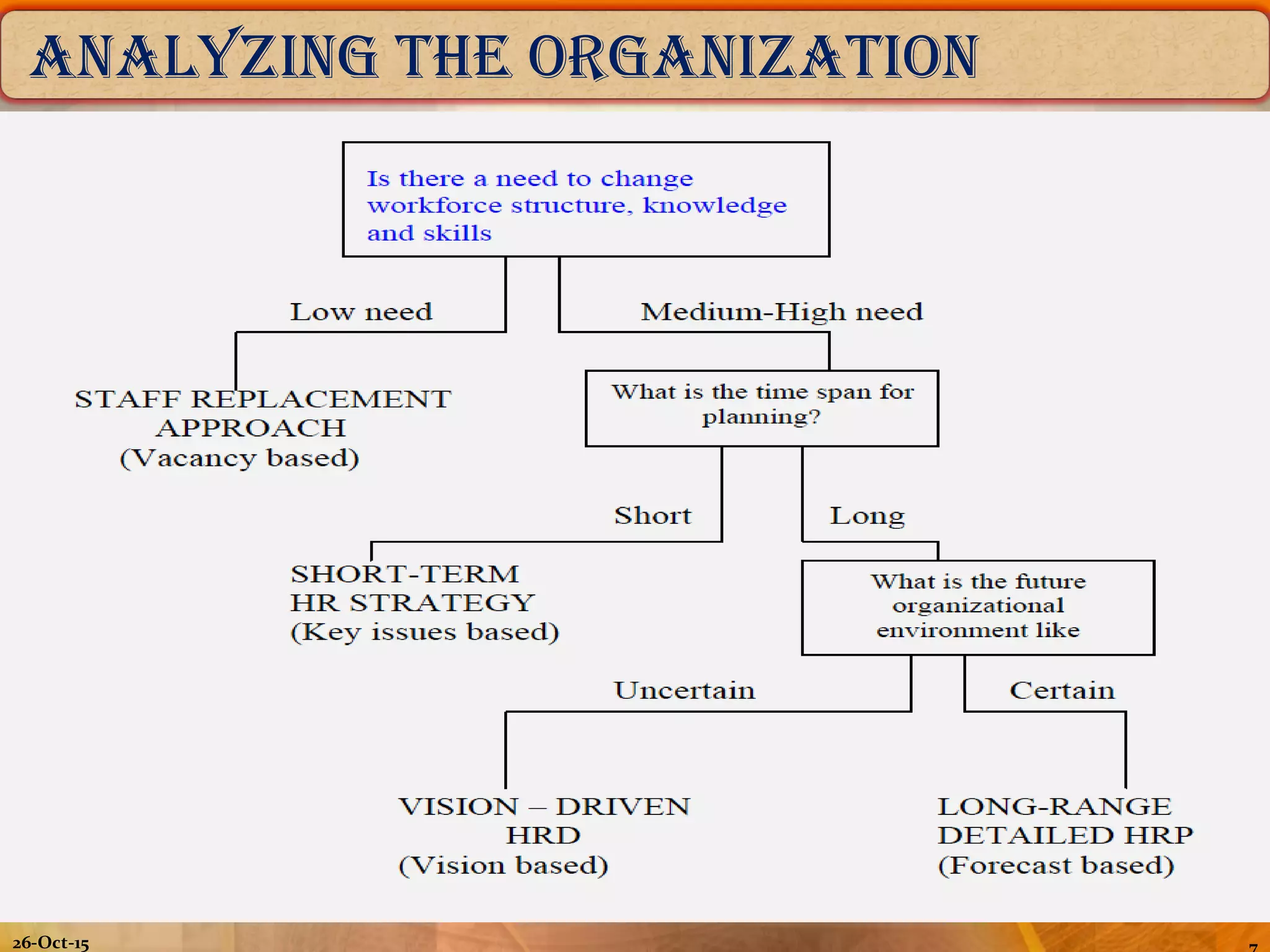
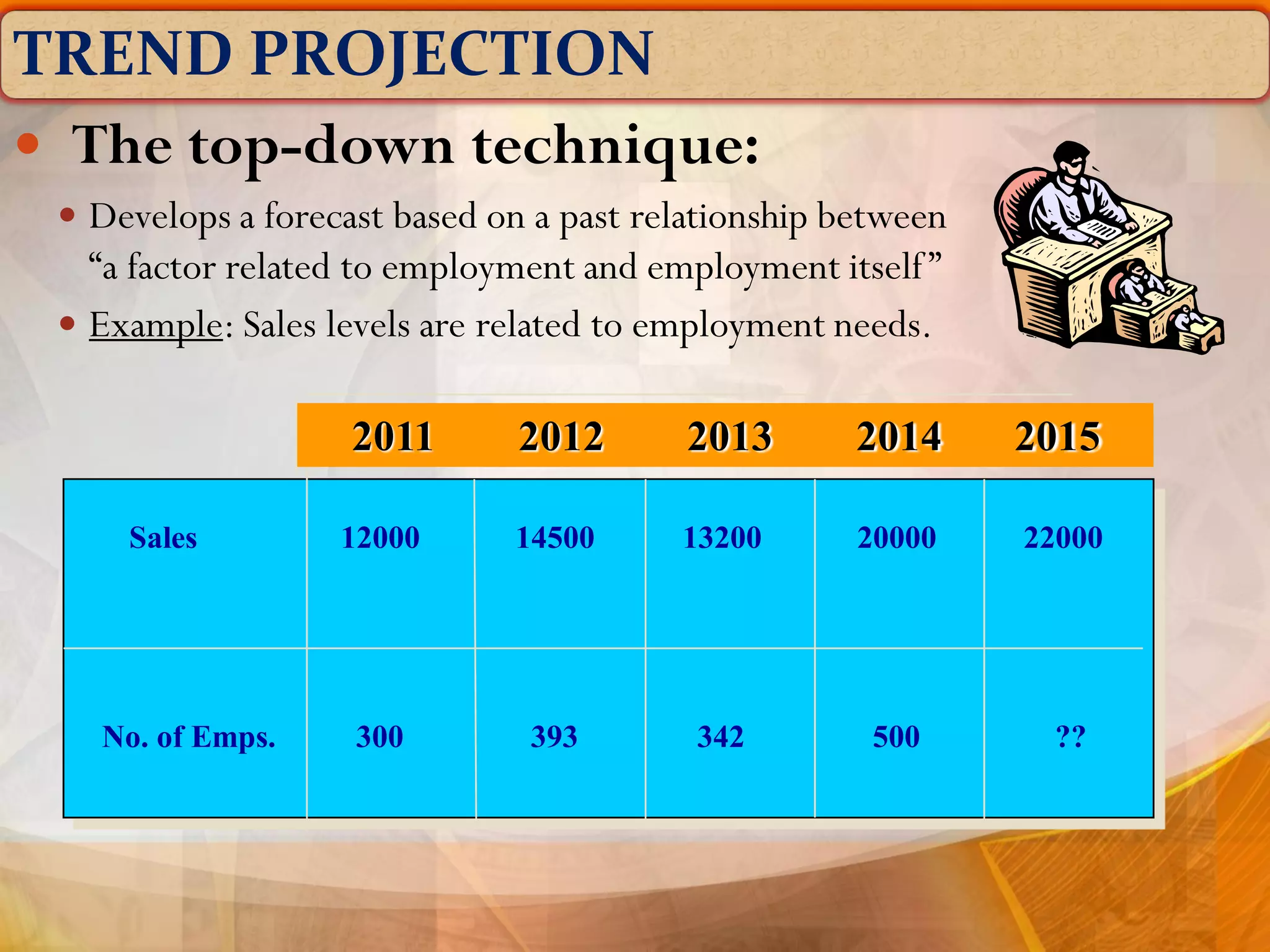
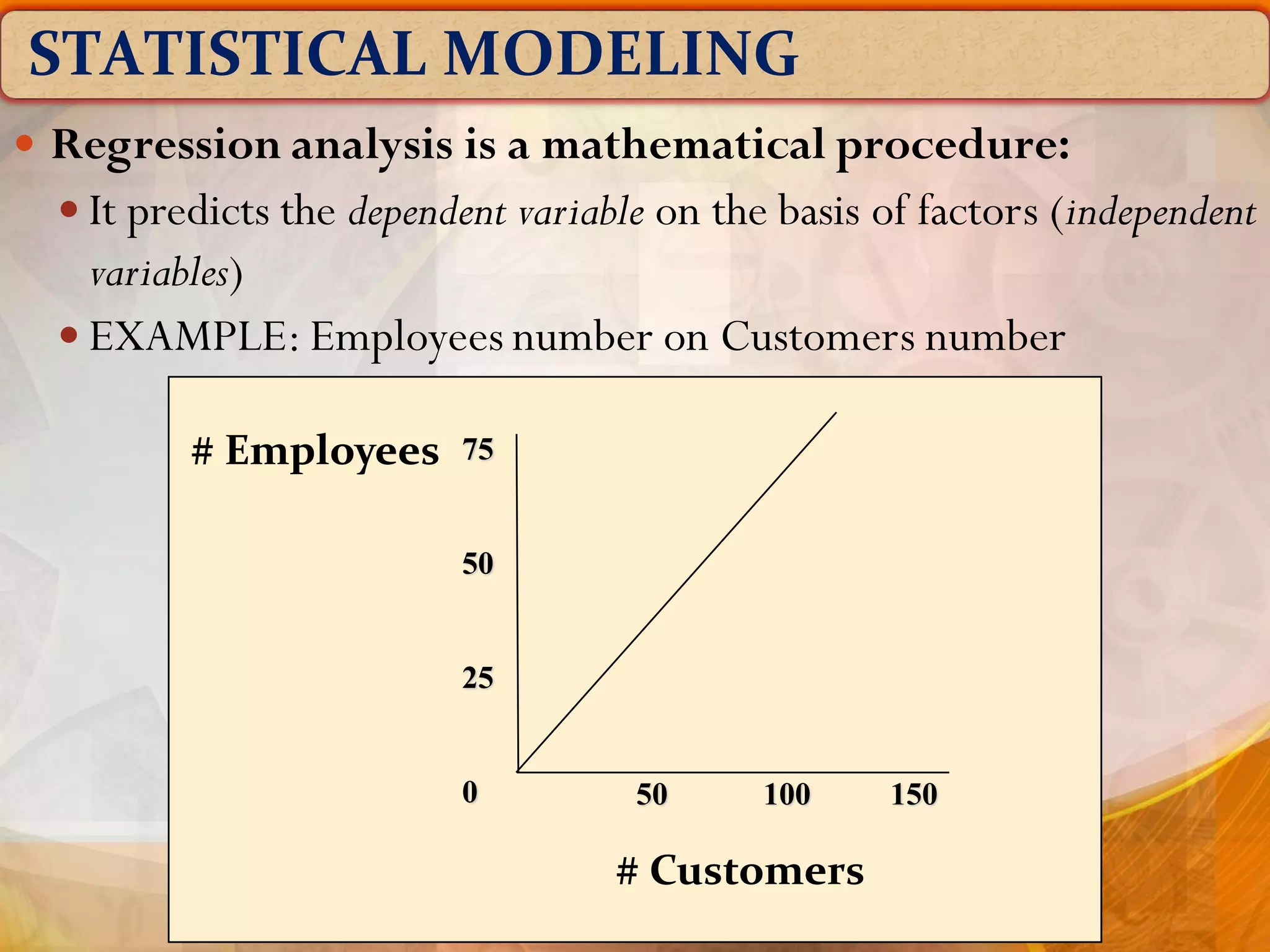
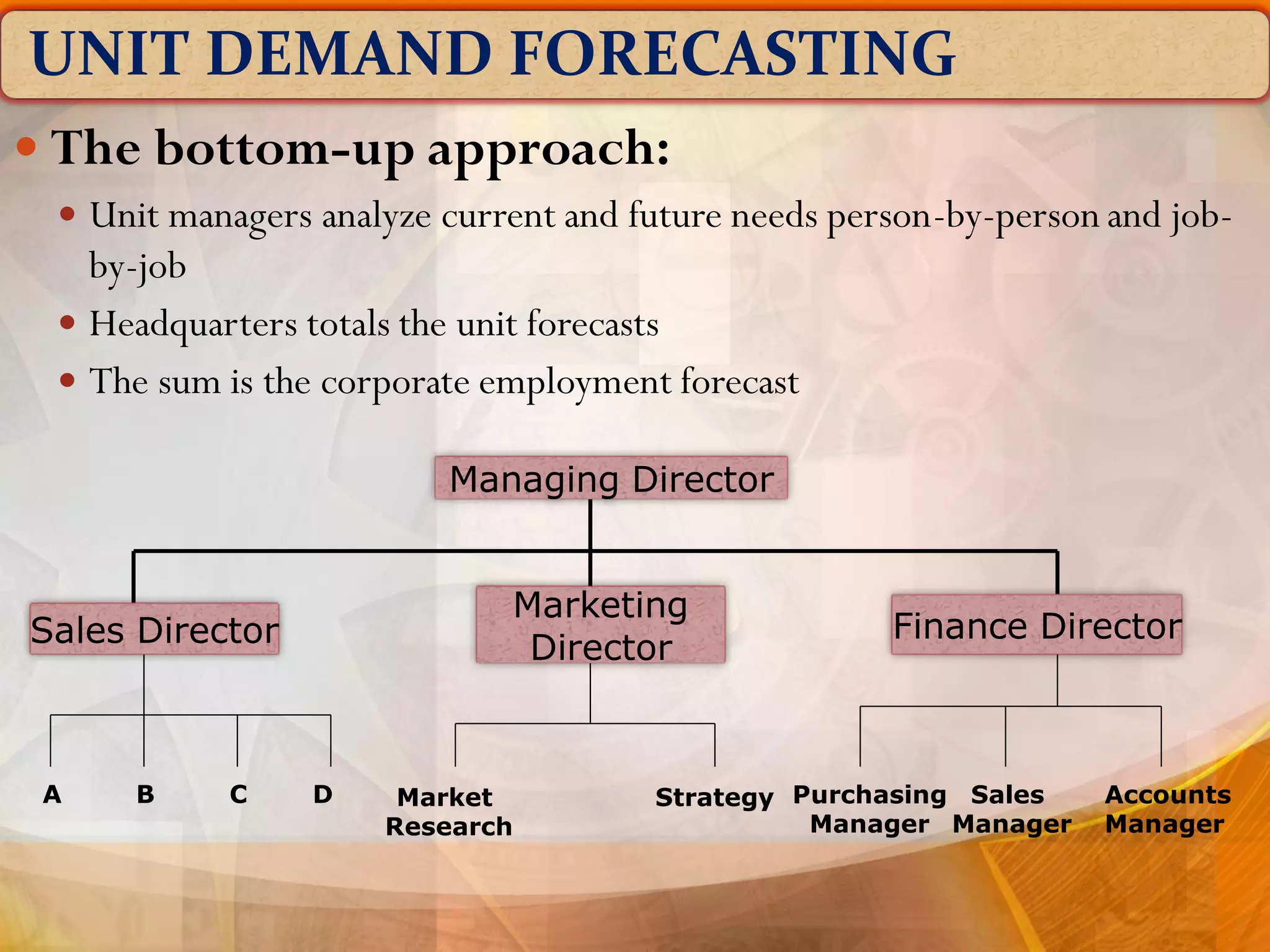
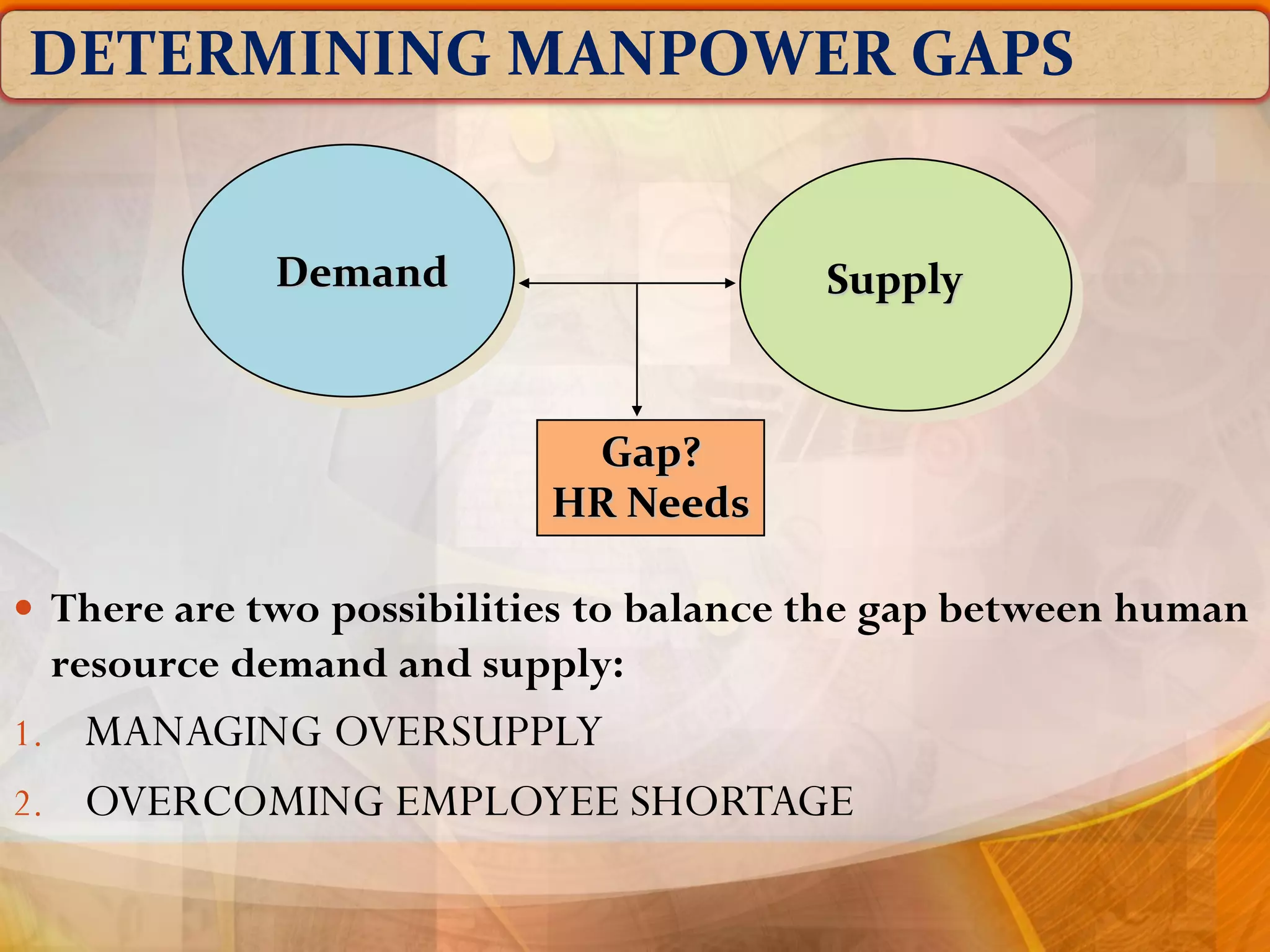
The document outlines the concept of manpower planning (MPP) as a crucial process for determining an organization's human resource needs. It details the steps involved in MPP, including demand and supply forecasting, and methods used for analysis, highlighting the importance of strategic planning in managing workforce requirements. Additionally, it emphasizes the significance of a Human Resource Information System (HRIS) for effective planning and tracking of human resources.