Embed presentation
Downloaded 208 times






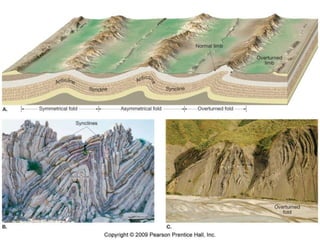







There are four main types of mountains based on their origin: 1) Fold mountains like the Himalayas and Andes are formed by the folding of crustal rocks under compressive forces. 2) Block mountains such as the Vosges and Black Forest are formed by faulting of the earth's crust. 3) Volcanic mountains including Kilavea volcano and Stromboli volcano are built up from accumulated volcanic materials. 4) Residual mountains such as the Aravalli and Nilgiri ranges are formed by differential weathering that removes softer rock layers and leaves behind harder rock.













