This document discusses disability and services for persons with disabilities in India. It provides definitions of disability and outlines India's community-based rehabilitation (CBR) approach. Some key points:
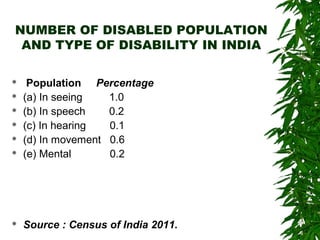
- According to the 2011 Census, there are 21 million persons with disabilities in India, comprising 2.1% of the population. The majority live in rural areas and have lower literacy and employment rates.
- India has implemented a CBR system to provide rehabilitation services within communities using local resources. However, there are still many challenges to effective implementation like poverty, stigma, and lack of trained professionals.
- The government has enacted laws promoting equal rights and opportunities for those with disabilities. It has also ratified the UN Convention on


![In India the socio-economic and cultural factors
create several hurdles in implementing CBR for
the PWD.
These constraints are as follows:-
1. Illiteracy and lack of awareness
2. Non availability of proper information or
guidelines
3. Poverty and over population
4. Misconceptions & Stigma.
5. Non acceptance and rejection of disables
like mentally challenged and mentally ill both at
urban as well as rural Society
6. Non-proximity of the Special Schools.
7. Lack of trained personnel.
8. Centralization of the services in Urban
areas -.
9.[1] scarcity of services In Urban area.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pptdisablesperson-141129060147-conversion-gate02/85/Ppt-disables-person-3-320.jpg)