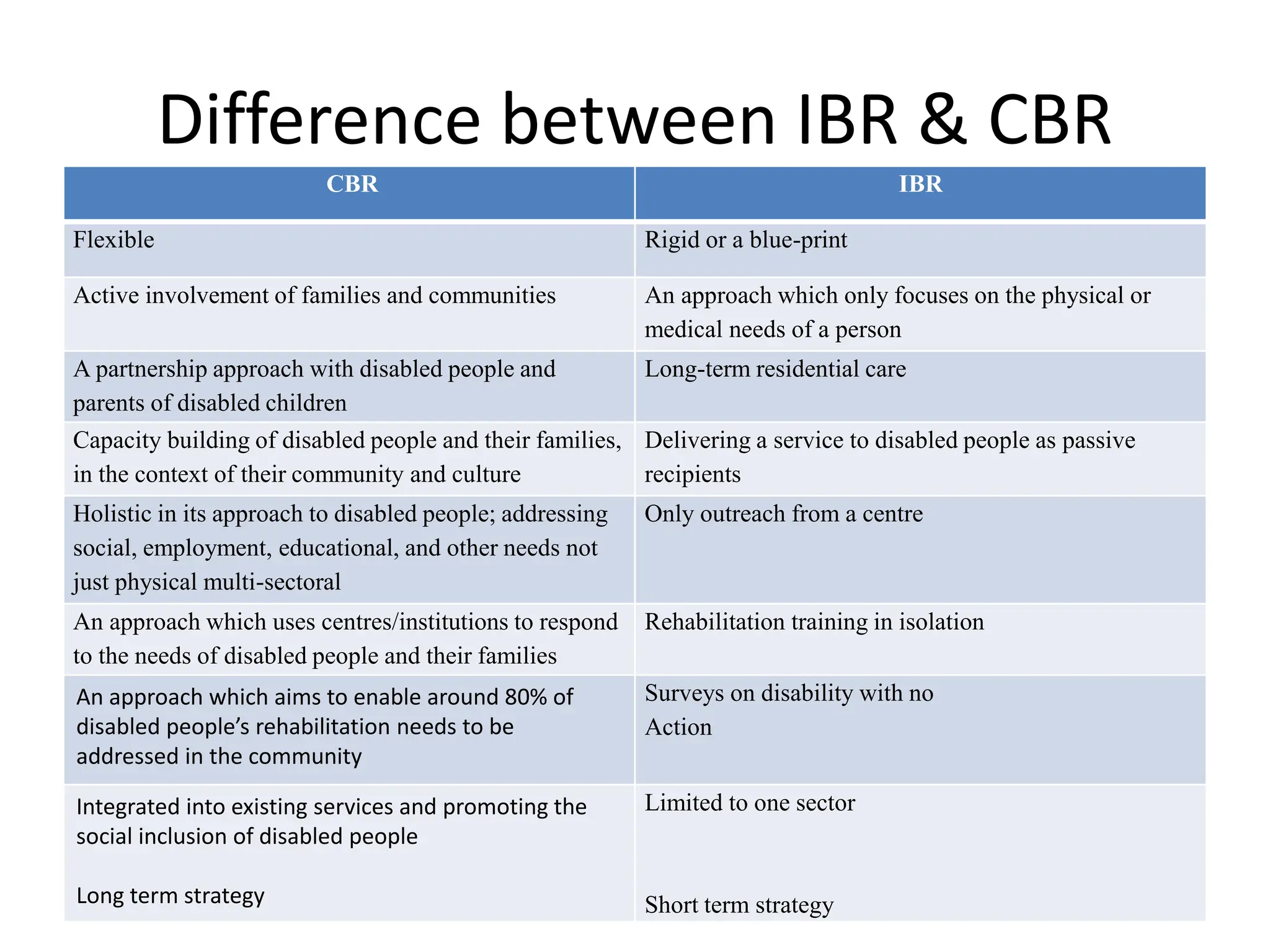
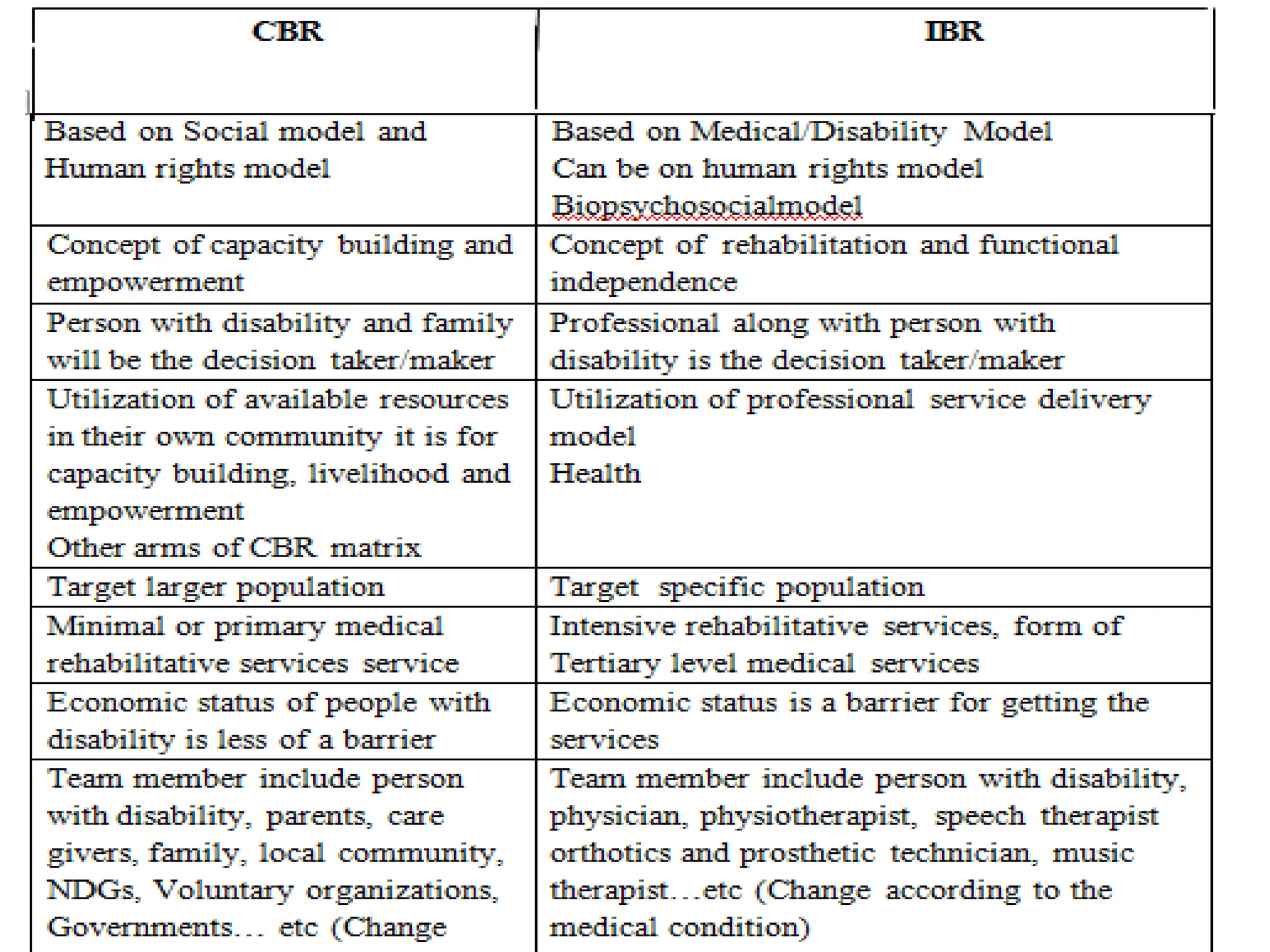
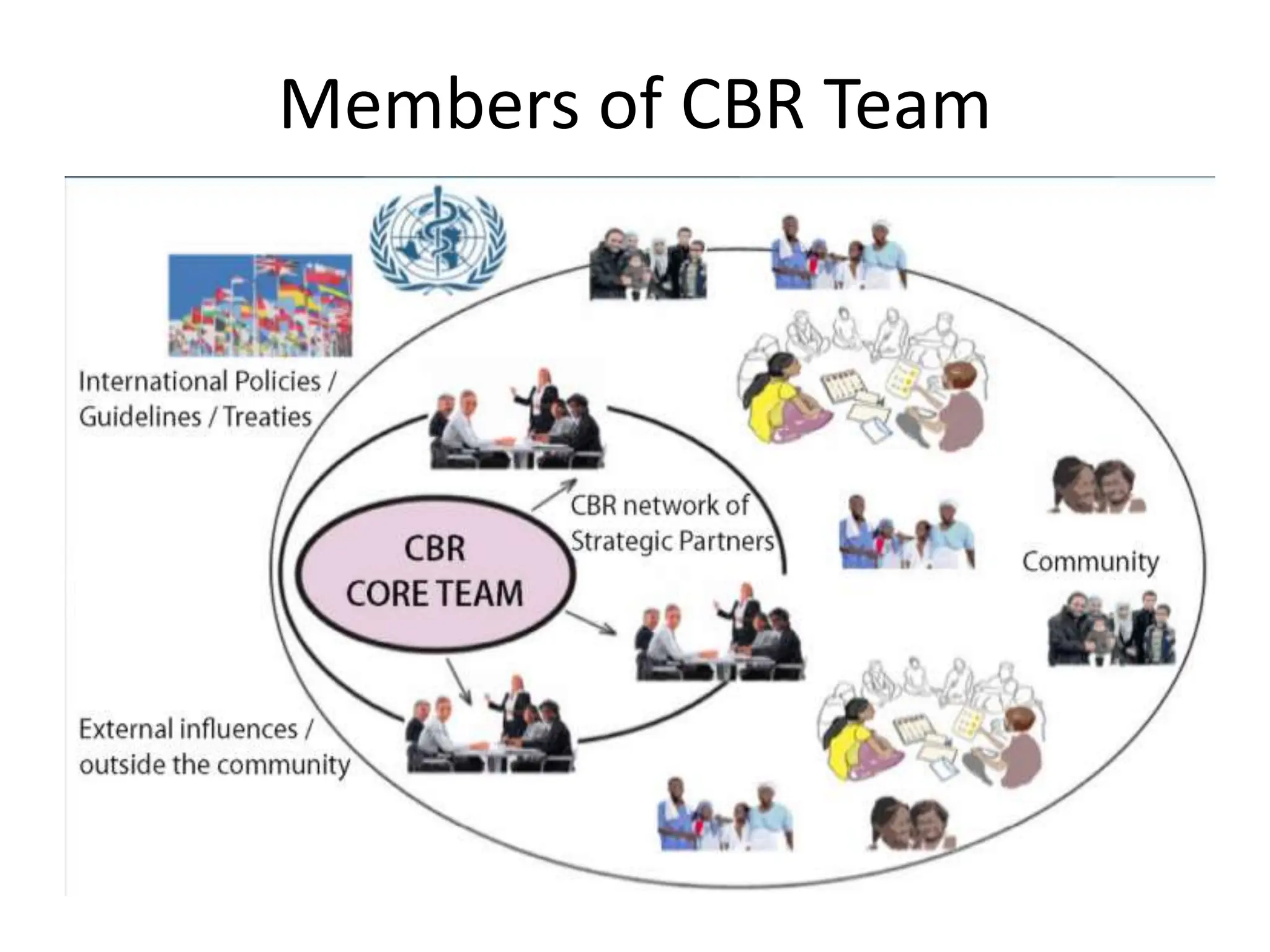
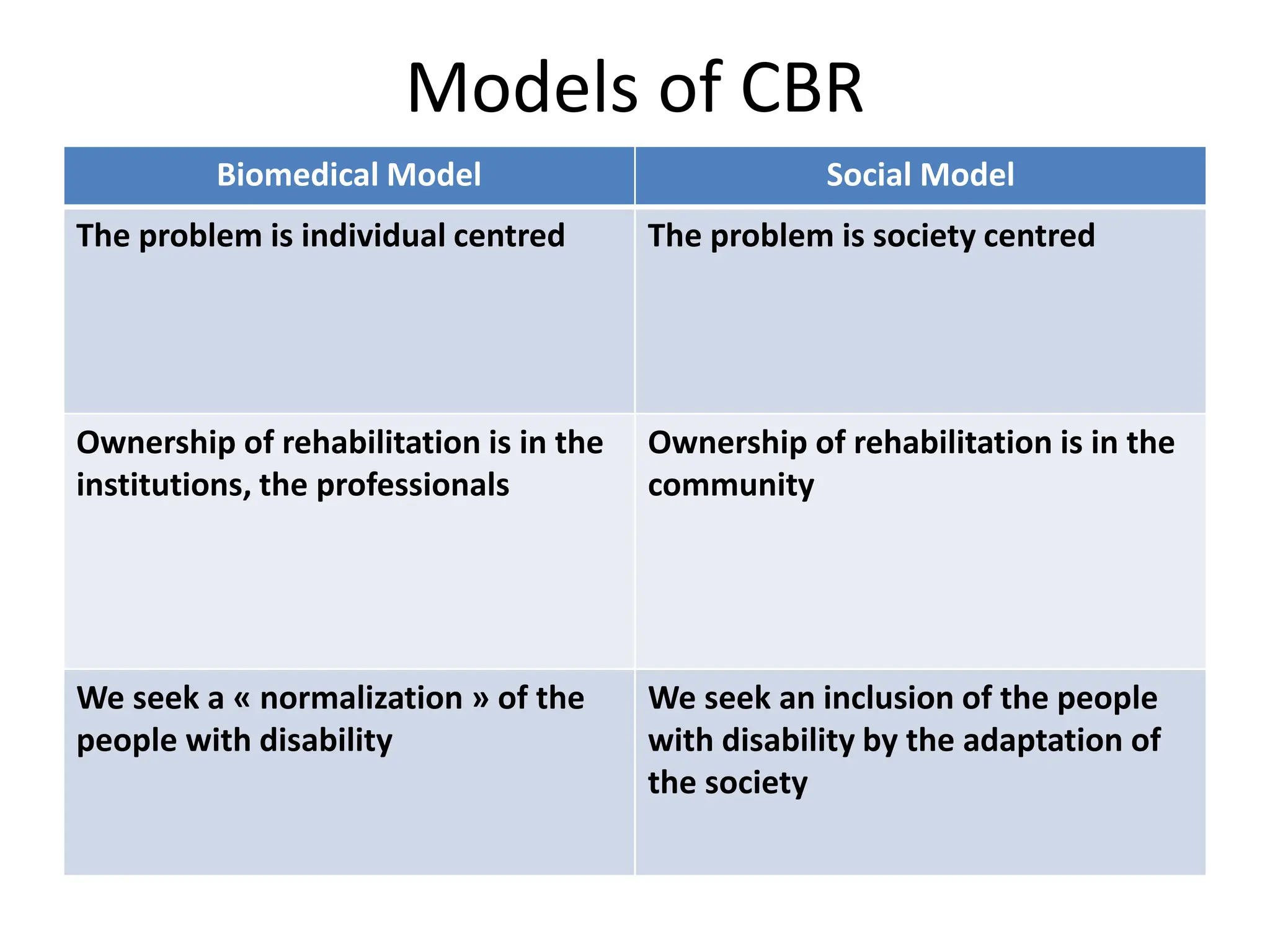
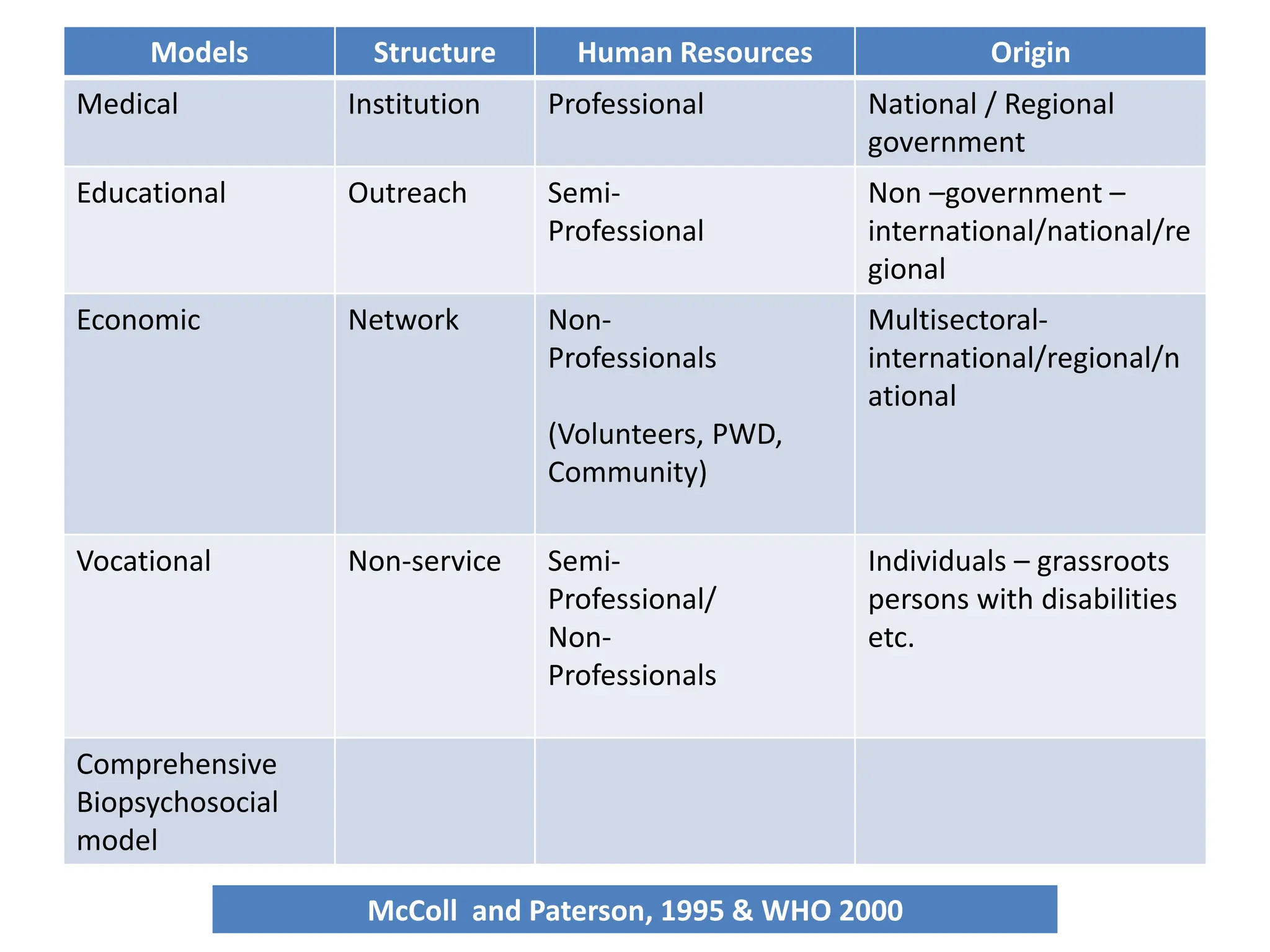
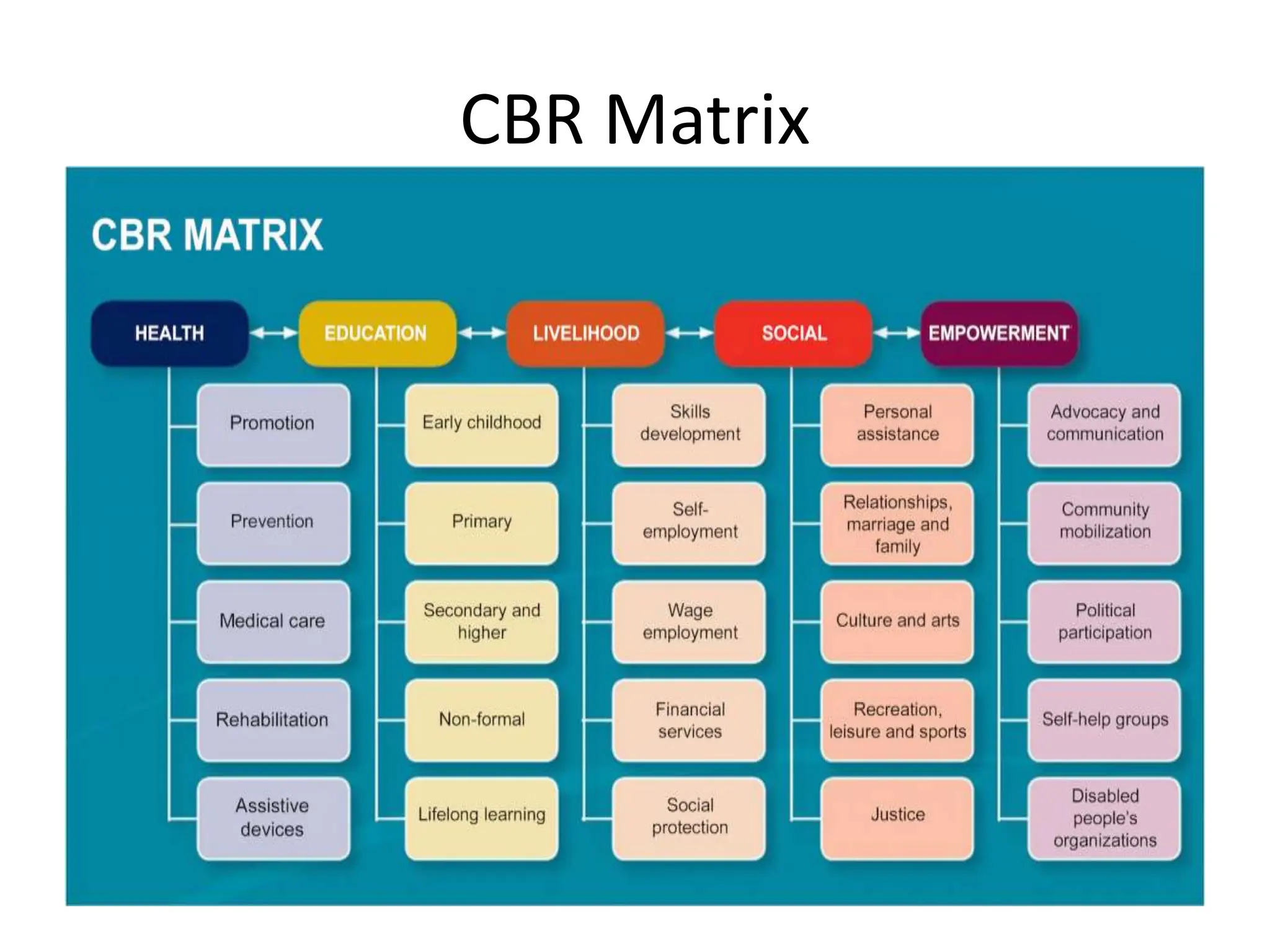
The document provides an overview of community-based rehabilitation (CBR), including its definition, concepts, need, objectives, models, and principles. CBR is a strategy that aims to improve the lives of people with disabilities through community involvement and development. It is implemented through partnerships between people with disabilities, their families, communities, and support services. The goals of CBR are to maximize abilities and ensure inclusion of people with disabilities in all aspects of community life.