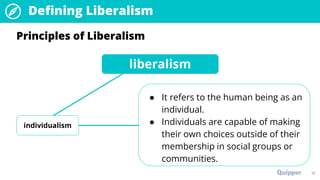
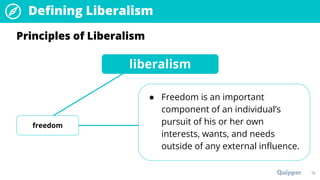
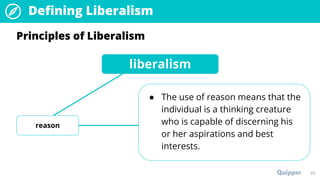
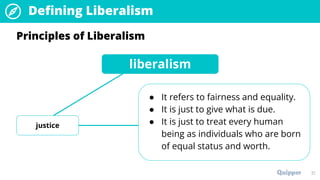
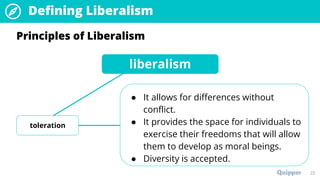
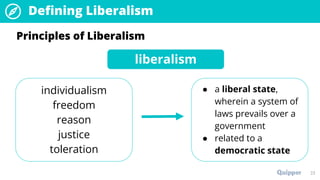
The document provides an overview of the political ideology of liberalism. It defines liberalism and discusses its key principles of individualism, freedom, reason, justice, and toleration. It then outlines the historical context in events like the English Civil War, American Revolution, and French Revolution that helped shape liberal thought. The document also profiles some of the main liberal thinkers like Locke, Mill, and Jefferson. It describes the variations of classical and modern liberalism. Overall, the summary provides background on the development and principles of liberalism as a foundational ideology.