1) Minerals are naturally occurring inorganic solids with a specific chemical composition and atomic structure, while rocks are aggregates of minerals or organic materials formed through various geological processes.
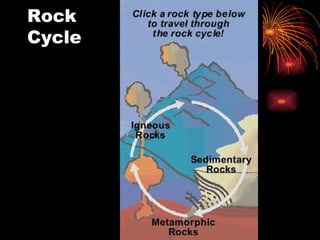
2) There are three main types of rocks: sedimentary rocks formed through accumulation and cementation of sediments, igneous rocks formed by cooling of magma or lava, and metamorphic rocks formed from pre-existing rocks subjected to heat and pressure.
3) Minerals can be identified based on properties like color, streak, hardness, cleavage, luster, fracture, and chemical composition. The three most common elements in minerals are aluminum, silicon, and oxygen. Rocks continuously change from one type to another through the rock