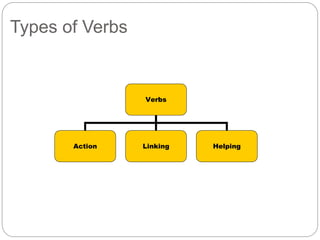
Verbs express actions, states of being, or events and come in several types. A verb can be an action verb that shows physical or mental activity, a linking verb that connects a subject to a predicate describing a state, or a helping verb that works with the main verb. Verbs are also regular or irregular in formation and can be dynamic, showing continuous action, or stative, showing a state of being. Proper subject-verb agreement requires matching a verb's number with its subject.