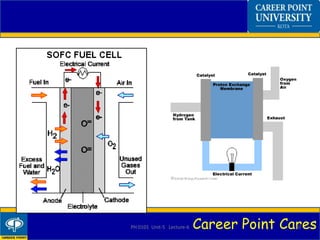
Fuel cells convert chemical energy from hydrogen into electrical energy through electrochemical reactions. A fuel cell has an anode, cathode, electrolyte, and catalyst. Hydrogen enters the anode and splits into protons and electrons. The protons pass through the electrolyte while the electrons power an external circuit. At the cathode, oxygen and the protons react to form water. Fuel cells have advantages like zero emissions and high efficiency but also disadvantages like high costs. Applications include portable power, transportation, and power distribution.