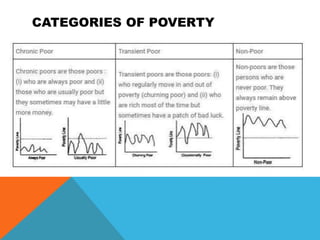
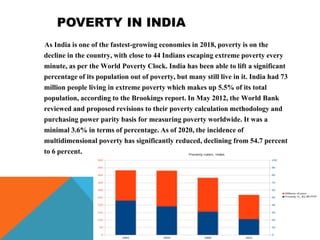
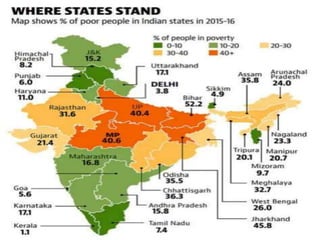
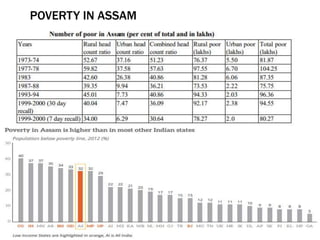
The document discusses poverty, outlining its definitions, types, and categories, as well as the poverty line measure and its significance. It highlights the state of poverty in India and specifically in Assam, noting improvements but significant challenges that remain. Causes of poverty in Assam are identified, along with proposed poverty alleviation programs aimed at economic growth and better resource distribution.