Embed presentation
Download to read offline






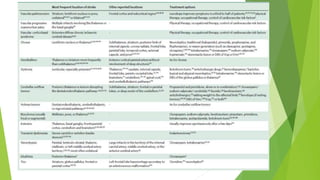


Post-stroke movement disorders can develop during or after a stroke. They include conditions like hemiballismus and tardive dyskinesia. The pathophysiology involves disruptions to motor control circuits in the brain from the stroke. Most cases spontaneously resolve within 6-12 months, but some patients require pharmacological treatment or even surgery for severe, persistent cases. Prognosis depends on factors like age of onset, duration of symptoms, and whether the movement disorder is generalized or localized.








