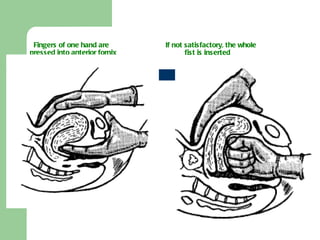
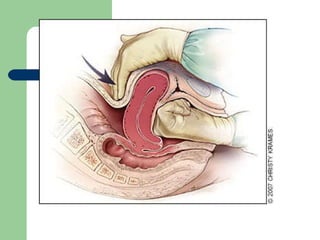
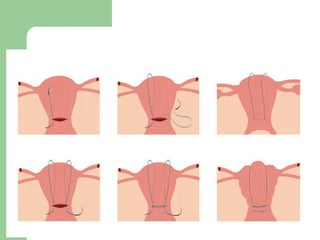
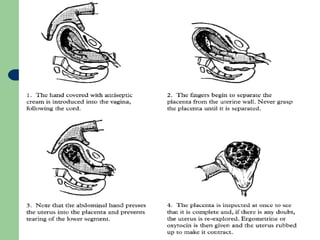
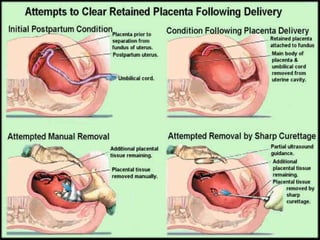
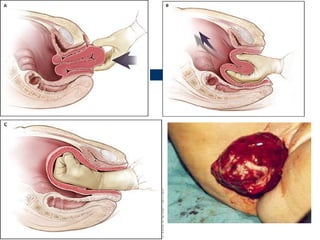
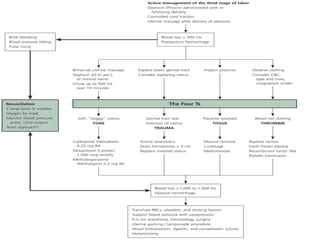
This document summarizes causes, risk factors, diagnosis, and management of postpartum hemorrhage (PPH). PPH is defined as blood loss of 500 ml or more within 24 hours of delivery. Common causes include uterine atony (70%), retained placenta, genital tract trauma, and bleeding disorders. Risk factors include previous uterine surgery, uterine abnormalities, and operative delivery. Diagnosis involves estimating blood loss and identifying the cause. Management involves resuscitation, arresting the bleeding through uterotonic drugs, manual removal of retained placenta, repairing lacerations, and in severe cases, surgical procedures like hysterectomy.