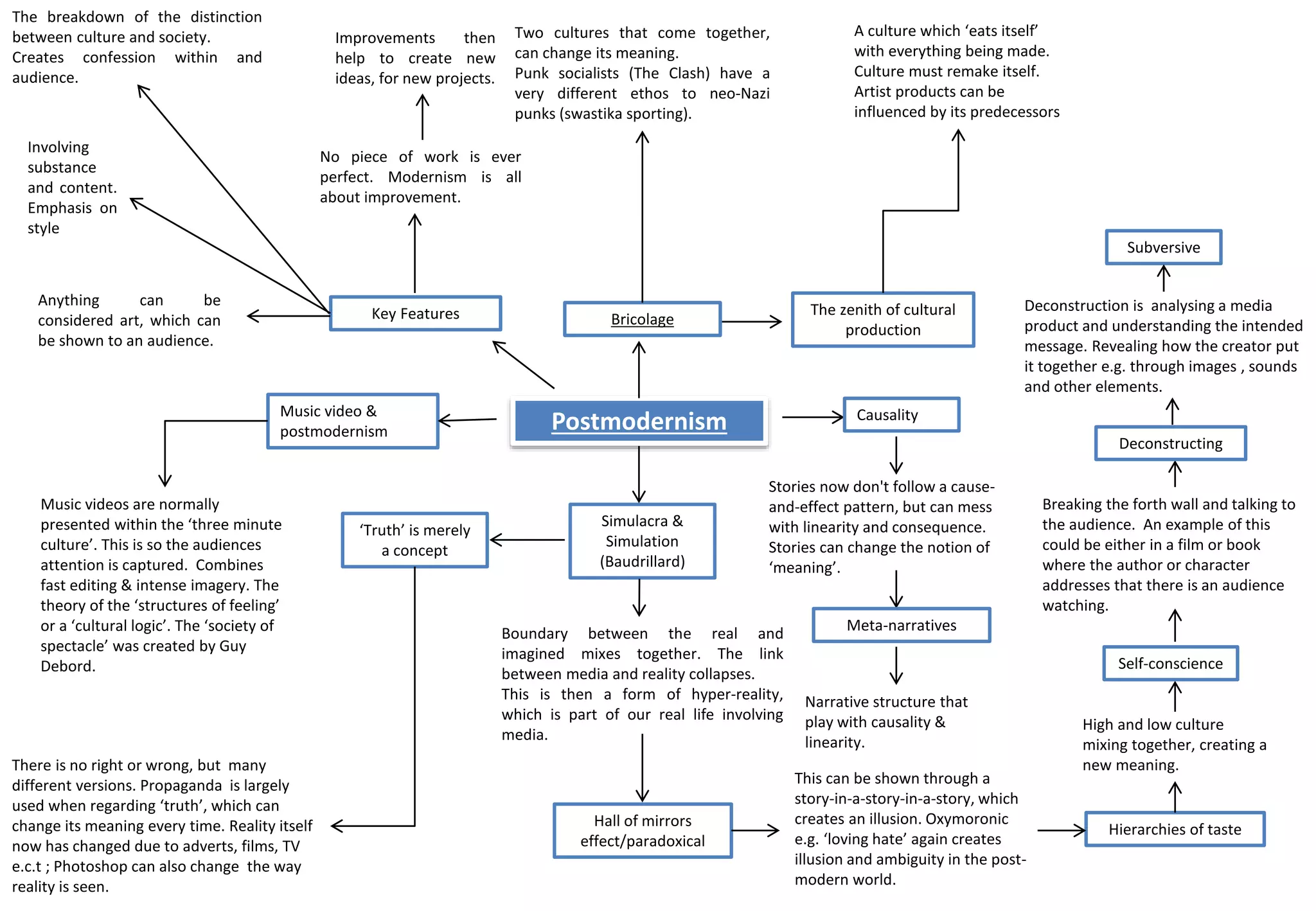
Postmodernism emphasizes style over substance and challenges traditional notions of art, truth, and linear narratives. Key aspects include the breakdown of distinctions between high and low culture, an emphasis on bricolage and mixing of cultural forms, and questioning of objective truths and meta-narratives through techniques like self-referentiality, deconstruction, and challenging hierarchies. Postmodern culture is characterized by constant remaking and influences between new and old works, with reality being blurred by media like music videos and photography.