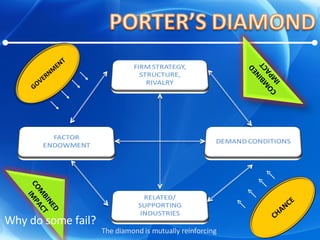
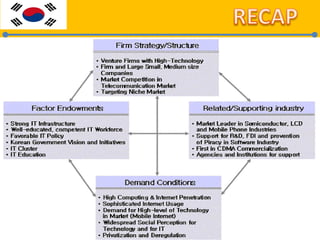
The document discusses Porter's Diamond model to explain why some nations, like Korea, succeed in international competition while others fail. It highlights key determinants such as demand conditions, factor endowments, support industries, firm strategy and rivalry, along with the influence of government and chance. Through case studies, particularly in the information and telecommunications sector, it illustrates Korea's competitive advantages and the importance of a favorable business environment and government policies for industry growth.