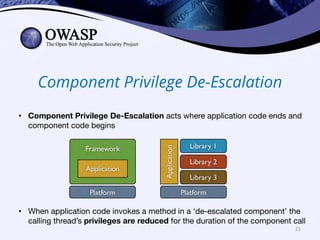
This document discusses popular approaches to preventing code injection attacks and argues they are inadequate. It introduces Tainted Lexical Analysis, Name-Space Layout Randomization, Component Privilege De-escalation, and Runtime Protection Rules as new techniques that can prevent code injection attacks without heuristics and provide always-on protection, virtual patching capabilities, and prevention of serialization vulnerabilities and API abuse. These techniques are presented as superior alternatives to traditional application security approaches.