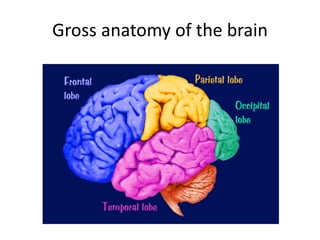
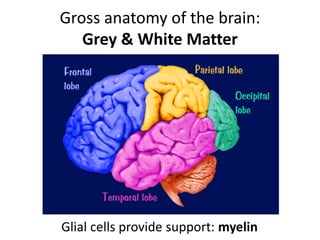
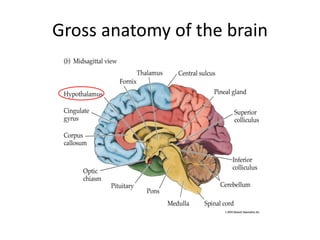
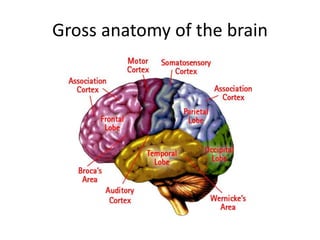
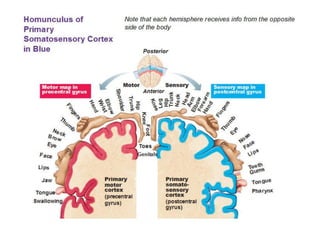
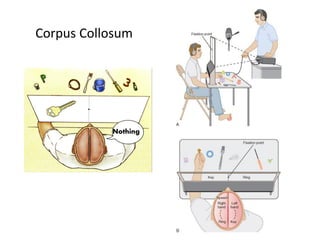
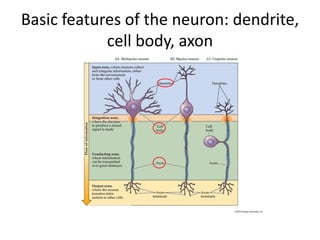
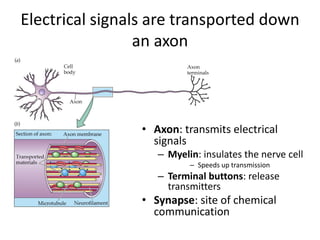
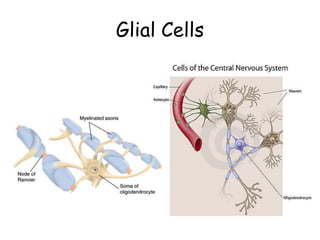
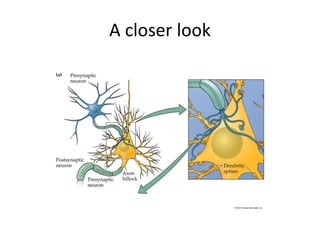
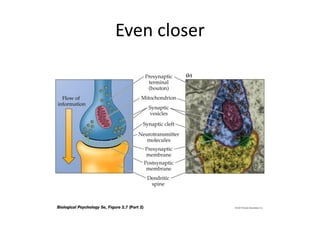
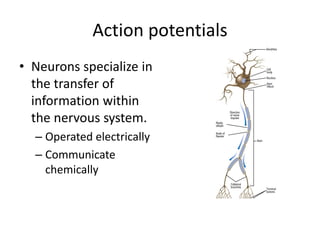
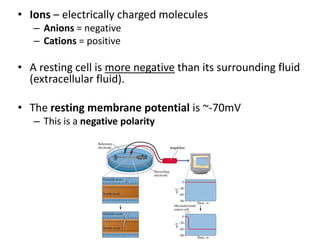
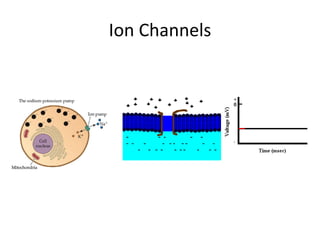
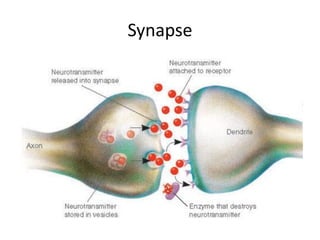
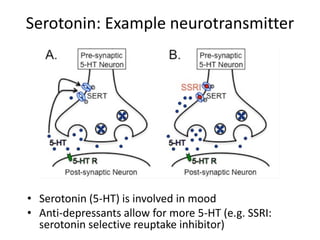
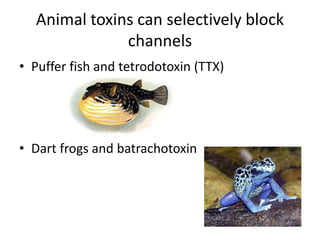
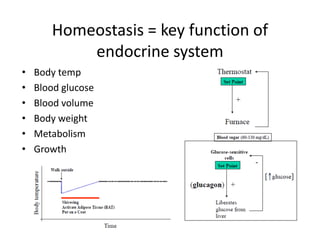
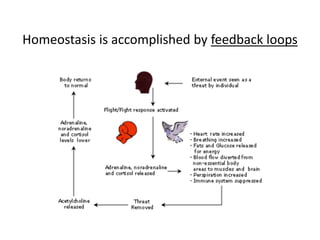
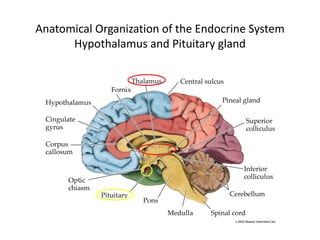
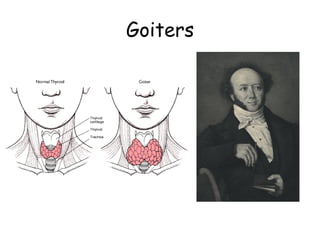
This document provides an overview of the neural basis of behavior. It discusses the gross anatomy of the brain including grey and white matter. It also describes the structure and function of neurons, including their parts like dendrites and axons. Action potentials and synaptic transmission between neurons are explained. The role of glial cells and myelin in supporting neurons is covered. Additionally, it discusses the endocrine system and how hormones influence behavior through feedback loops and homeostasis. Finally, it introduces the field of behavioral genetics and different research methods used to study genetic influences on behavior.