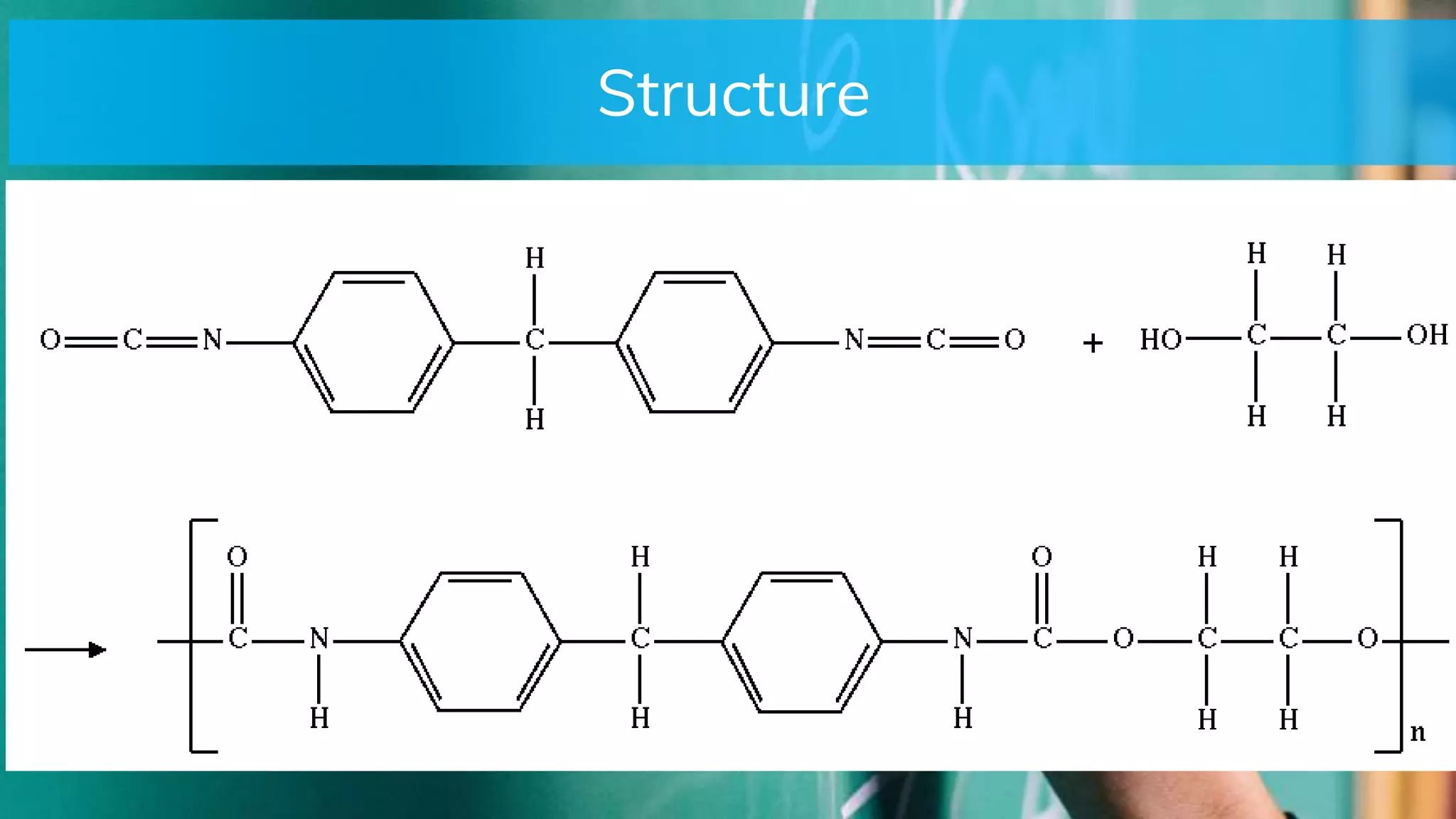
This document discusses polyurethane, its history, properties, applications in biomedical engineering, and advantages and disadvantages for medical use. Polyurethane was discovered in 1937 and is formed from reacting a polyol with a diisocyanate. It has since been used in applications like aircraft insulation, prosthetics, catheters, and artificial hearts due to its biocompatibility and mechanical properties like tensile strength. However, long term use can lead to degradation issues. Overall, polyurethane is a versatile material that is widely researched for medical devices due to its tunable surface properties.