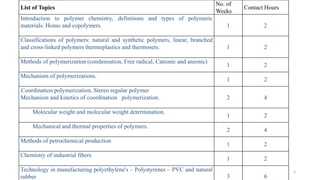
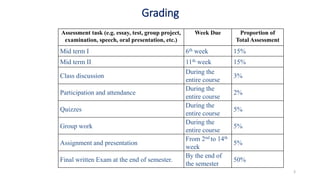
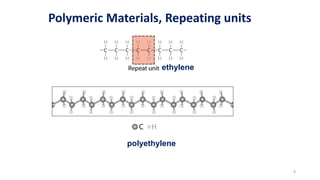
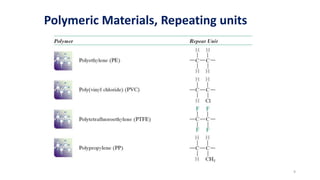
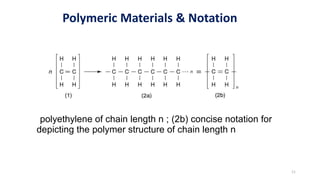
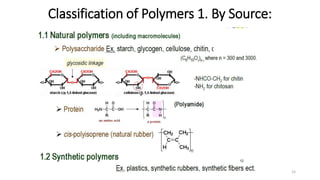
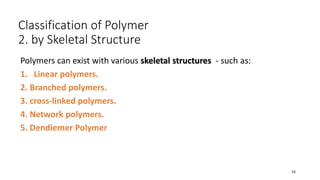
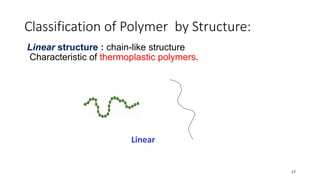
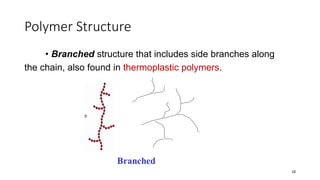
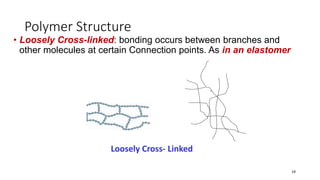
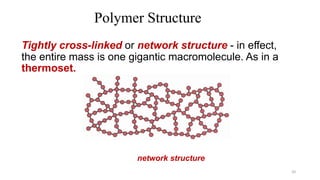
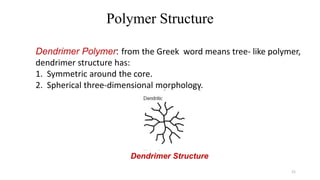
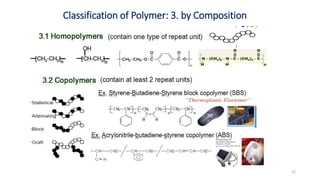
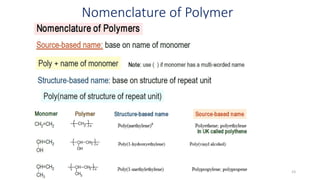
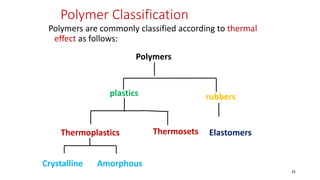
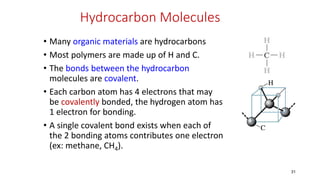
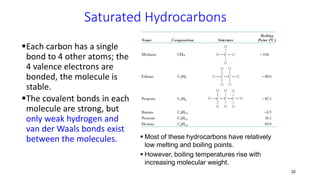
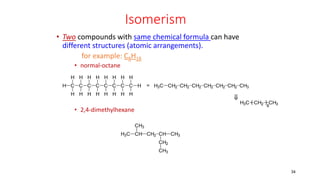
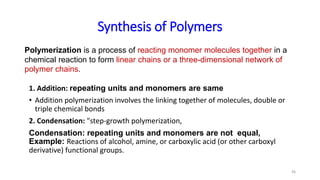
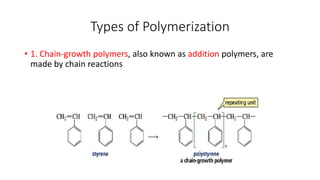
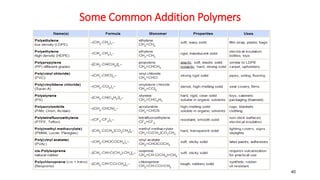
Polymerization is a process of reacting monomer molecules together to form polymer chains. There are two main types of polymerization:
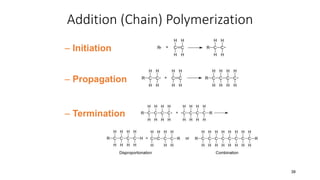
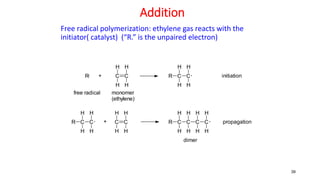
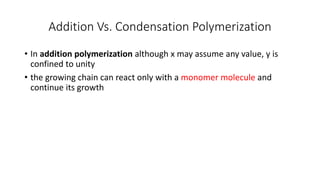
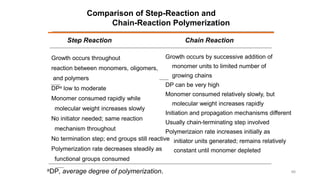
1) Addition (chain) polymerization involves linking monomers together through double or triple bonds. It includes initiation, propagation, and termination steps.
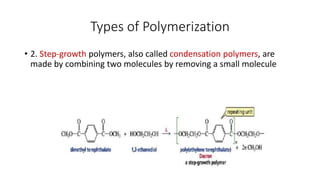
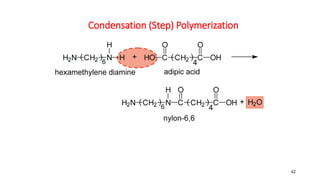
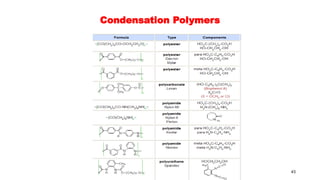
2) Condensation (step-growth) polymerization combines monomers by removing a small molecule, like in polyester formation. It does not involve chain growth.
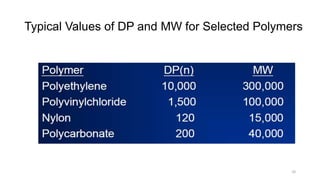
Condensation polymerization has a lower degree of polymerization and molecular weight increases slowly as functional groups are consumed in each step. In contrast, addition polymerization can achieve very high degrees of polymerization and molecular weight increases rapidly through successive monomer additions to growing chains.