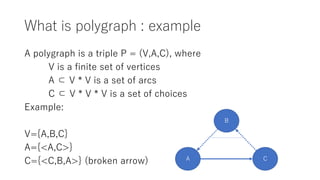
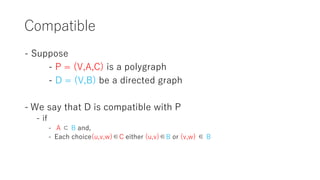
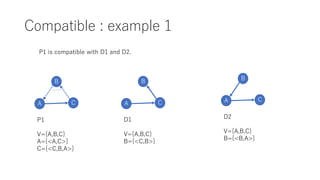
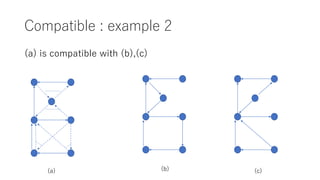
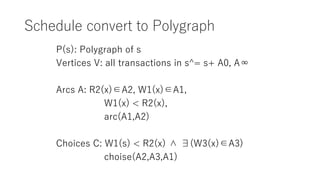
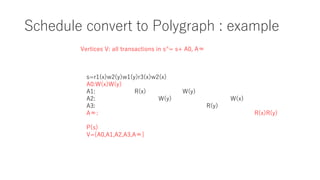
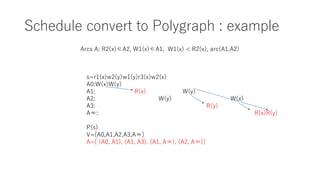
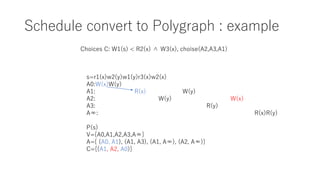
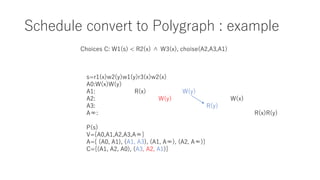
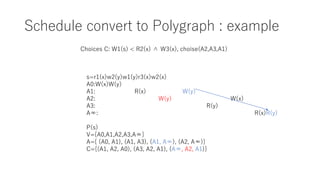
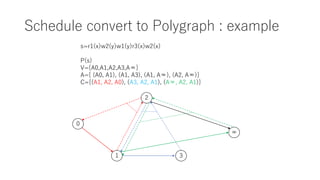
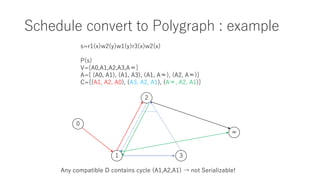
The document discusses converting a schedule validation problem into a polygraph problem to leverage existing polygraph algorithms. It defines what a polygraph is - a triple of vertices, arcs, and choices. It then explains how to construct a polygraph P(s) from a schedule s by making transactions vertices and enforcing ordering/conflict relationships with arcs and choices. Testing if a schedule is conflict-serializable amounts to checking if the corresponding polygraph P(s) has a compatible acyclic directed graph - if so, it is serializable. An example converts a sample schedule into a polygraph to check for cycles.