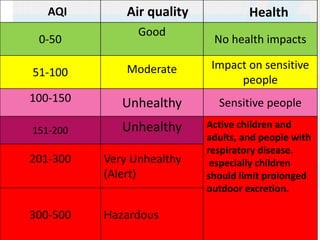
The document discusses pollution, its types, causes, and effects on the environment and human health, categorizing it into air, water, noise, and other forms. It highlights pollutants' impact, including respiratory diseases, ecosystem damage, and the importance of pollution control measures such as regulations and public awareness. The document emphasizes the need for preventive action and technological solutions to mitigate pollution's adverse effects.