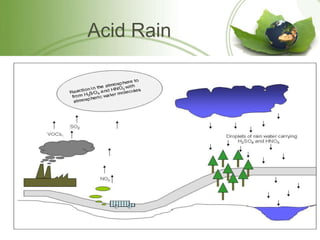
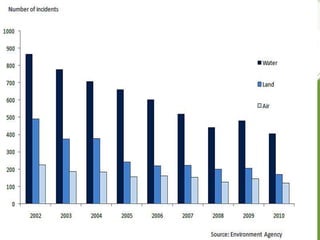
This document discusses different types of pollution including air, water, noise, light, and soil pollution. It defines each type of pollution and provides examples of sources and effects. For each type of pollution, it also discusses ways to control and prevent further pollution, such as maintaining a healthy distance between industrial and residential areas for air pollution, conserving water and properly disposing of waste to prevent water pollution, limiting noise from vehicles and machinery to reduce noise pollution, and treating industrial and agricultural waste to control soil pollution. The document aims to raise awareness about the different types of pollution and measures that can be taken to address pollution issues.