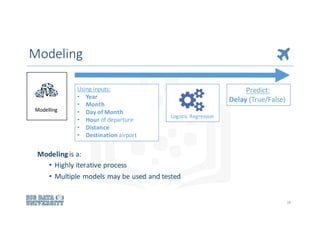
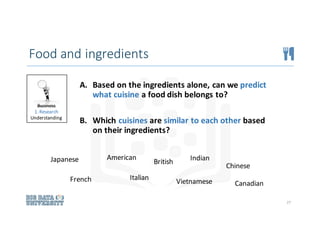
The document outlines a comprehensive approach to solving data science problems, focusing on a methodology that starts with business understanding and follows through to model evaluation and feedback. It illustrates the application of this process using examples such as predicting flight delays and classifying cuisines based on ingredients. Key elements include defining project objectives, data preparation, model selection, and iterative evaluation for deployment.





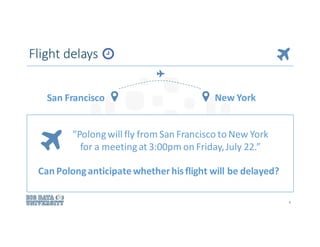

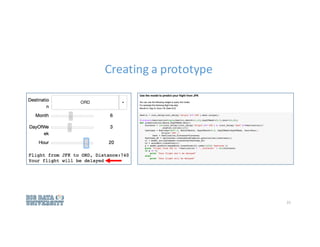
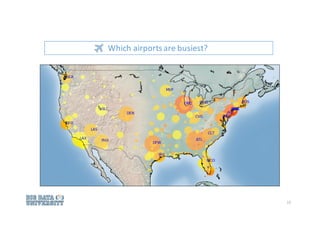
![Using departing & arrival airport, date, carrier, etc.,
we could predict flight [DELAY] or [NO-DELAY] using
logistic regression.
• Identify suitable statistical/machine learning technique(s)
10
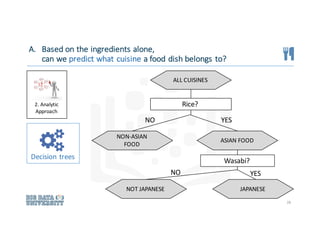
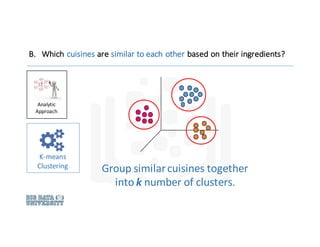
2. Analytic
Approach
• Linear regression
• Logistic regression
• Clustering
• Decision Trees
• Principal component
analysis
• Text analysis
• SVM/SVR
• Neural networks
• Dimension
Reduction
2. Analytic approach](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polonglin-howtoapproachdatascienceproblemsfromstarttoend-160716094311/85/Polong-Lin-how-to-approach-data-science-problems-from-start-to-end-10-320.jpg)

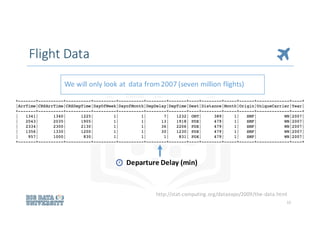
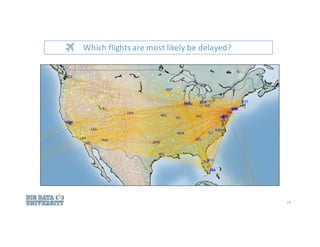
![Data Preparation typically includes:
• Data cleaning
• Merging data
• Transforming data
• Feature engineering
• Text analysis
15
6. Data preparation
6. Data
Preparation
Flights are classified as “delayed” if >15 min late.
• Delayed? [True or False]
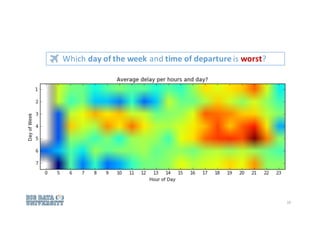
Does time of day for departure predict delays?
• Hour](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polonglin-howtoapproachdatascienceproblemsfromstarttoend-160716094311/85/Polong-Lin-how-to-approach-data-science-problems-from-start-to-end-15-320.jpg)